What is Bronchitis?
An inflammation of the bronchi, the airways that transport air to and from the lungs, is known as bronchitis. In addition to irritants like dust, smog, and cigarette smoke, it may result from a bacterial or viral infection. Breathlessness, pressure in the chest, coughing, and wheezing are all signs of bronchitis. The most common short form for bronchitis is bronch .
An inflammation of the bronchi, the airways that transport air to and from the lungs, is known as bronchitis. It may be chronic, enduring a longer duration, or acute, enduring a shorter time.
Table of Contents
Types of Bronchitis
Acute Bronch: The most prevalent kind of bronchitis, known as acute Bronch, is typically brought on by a viral infection. Usually, the symptoms go away in a week or two.
Chronic Bronch: This is a chronic illness that lasts for two years and is defined by a persistent cough and mucus production for at least three months of the year. It is frequently linked to pollution from the environment and smoking.
Causes of Bronchitis
Viruses: A viral infection, such as the flu, respiratory syncytial virus, or the common cold, is the most frequent cause of acute Bronch (RSV).
Bacteria : Although they are less frequent than viral infections, bacteria can nevertheless result in Bronch . One of the most frequent offenders is Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Irritants: Bronch can be brought on by exposure to irritants such as fumes, dust, air pollution, and cigarette smoke.
Allergies: Bronch can be brought on by allergies to mold, dust mites, pollen, and other allergens.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): The irritation of the airways caused by stomach acid reflux might result in Bronch.
Pathophysiology
Inflammation: The bronchi’s lining swells and becomes inflammatory, which narrows the airways. The body’s immunological reaction to an infection or inflammation causes this.
Production of Mucus: Excess mucus is produced by the irritated airways, which can worsen airflow obstruction and cause coughing.
Bronchospasm: This is a condition when the muscles that surround the airways contract, making breathing more difficult and further restricting the path.
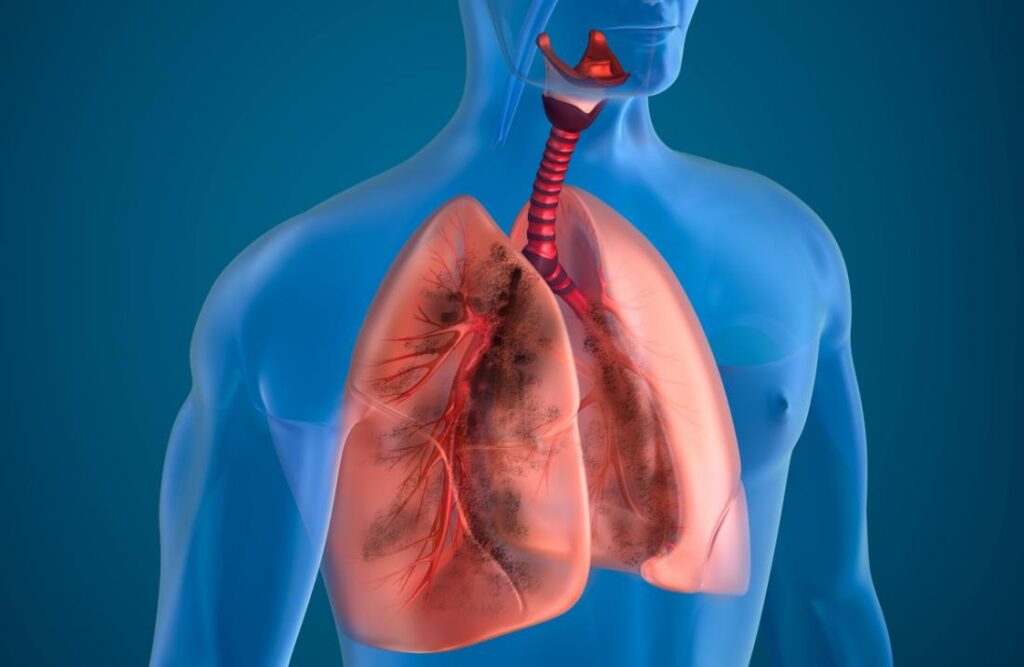
Clinical Features
Acute Bronch
Cough: This is the most prevalent symptom and is typically characterized by a dry, hacking cough that, as the infection worsens, can become productive and produce phlegm.
Wheezing: Making a whistling noise during breathing, especially when exhaling.
Pain or pressure in the chest: Tightness or pressure in the chest.
Breathing difficulties: Having trouble breathing, particularly when laying down.
Fever: There could be a slight fever going on.
Fatigue: A state of being weary and feeble.
Chronic Bronch
Persistent Cough : A persistent cough is defined as one that persists for two consecutive years for at least three months out of the year.
Sputum production: Depending on the cause, coughing up phlegm might be clear, white, yellow, or green in color.
Wheezing: Making a whistling noise during breathing, especially when exhaling.

Breathing difficulties: Having trouble breathing, particularly when exercising.
Tightness or pressure in the chest: A sensation of tightness in the chest.
Recurrent respiratory infections: Individuals who have chronic Bronch are at a higher risk of developing new respiratory infections.
Diagnostic Evaluation
History and Physical Exam: The physician will inquire about your past medical history, current symptoms, and any possible triggers. In order to evaluate your breathing and listen to your lungs, they will also do a physical examination.
Chest X-ray: Can be performed to rule out pneumonia and other lung diseases.
Sputum Culture: A sample of your phlegm, or sputum, will be tested for bacteria if a bacterial illness is suspected.
Spirometry: A test used to gauge the degree of airflow blockage by measuring lung function.
Treatment
Acute Bronch
Symptom relief and supportive care are the main goals of treatment for acute Bronch. This could consist of:
Rest: By taking a break, your body can concentrate on battling the infection.
Fluids: Consuming a lot of water thins mucus and reduces coughing.
Over-the-counter medications: Pain medicines such ibuprofen or acetaminophen can lower fever and pains. Expectorants or cough suppressants may offer momentary relief from coughing.
Chronic Bronchitis
The goals of treatment for chronic bronchitis are to control symptoms, avoid flare-ups, and reduce the rate of illness development. This could consist of:
Cessation of smoking: In order to effectively treat chronic bronchitis, smoking must end.
Medication: Inhaled corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, bronchodilators to open up the airways, and antibiotics if a bacterial infection is present.
Oxygen Therapy : In cases where oxygen levels are low, oxygen therapy may be required.
Pulmonary rehabilitation : A program that helps with breathing exercises and physical fitness is called pulmonary rehabilitation.
Prevention
Avoid exposure to irritants : Steer clear of irritants by avoiding dust, odors, air pollution, smoking, and secondhand smoke.
Wash your hand frequently : Hand washing is a good way to stop the viruses that cause bronchitis from spreading.
Vaccinate yourself: Influenza is a common cause of bronchitis. The flu vaccine can help protect you against influenza.
Keep up a healthy lifestyle: You may boost your immunity and stave off bronchitis by eating a balanced diet, exercising frequently, and getting enough sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What do you mean by Bronchospasm?
Bronchospasm is a condition when the muscles that surround the airways contract, making breathing more difficult and further restricting the path.
What are the types of Bronch?
The types of Bronch are,
Acute Bronch
Chronic Bronch
What are the prevention of Bronch ?
The prevention of Bronch are,
Avoid exposure to irritants
Wash your hand frequently
Vaccinate yourself
Related Articles