Angiosperms, or blooming plants, reproduce using a complex process that includes both sexual and asexual systems. Angiosperm reproductive systems are highly specialized and optimized for pollination and seed development. The reproductive structures in angiosperms are highly specialized and adapted to facilitate pollination and seed development. Here’s an overview of the key aspects of angiosperm reproduction and their reproductive structures:
Table of Contents
Reproduction in Angiosperm
Reproduction in angiosperms, or flowering plants, is the process by which these plants generate offspring to ensure the survival of their species. This procedure can occur in both sexual and asexual ways. Reproduction in angiosperms is the biological process by which flowering plants produce offspring, either through sexual reproduction, which involves the formation and fusion of male and female gametes to produce seeds, or through asexual reproduction mechanisms such as vegetative propagation and apomixis, which produce genetically identical clones of the parent plant.
Sexual Reproduction in Angiosperms
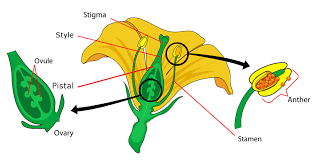
Flower Structure
Angiosperms’ principal reproductive structure is the flower, which is made up of various sections.
- Sepals are the outermost components of the flower, usually green, that guard the flower bud before it opens.
- Petals are often brilliantly colored to attract pollinators and are found just inside the sepals.
- Stamens are male reproductive organs that consist of:
- Anthers produce pollen grains containing male gametes.
- Filament: A structure that supports the anther.
4. The female reproductive organ, the pistil (or carpel), is made up of:
- Stigma: The sticky top component that collects pollen.
- Style: The stalk that joins the stigma and the ovary.
- Ovary: Contains ovules, which grow into seeds when fertilized.
Pollination
Pollination refers to the transport of pollen from the anther to the stigma. It can occur via a variety of agents:
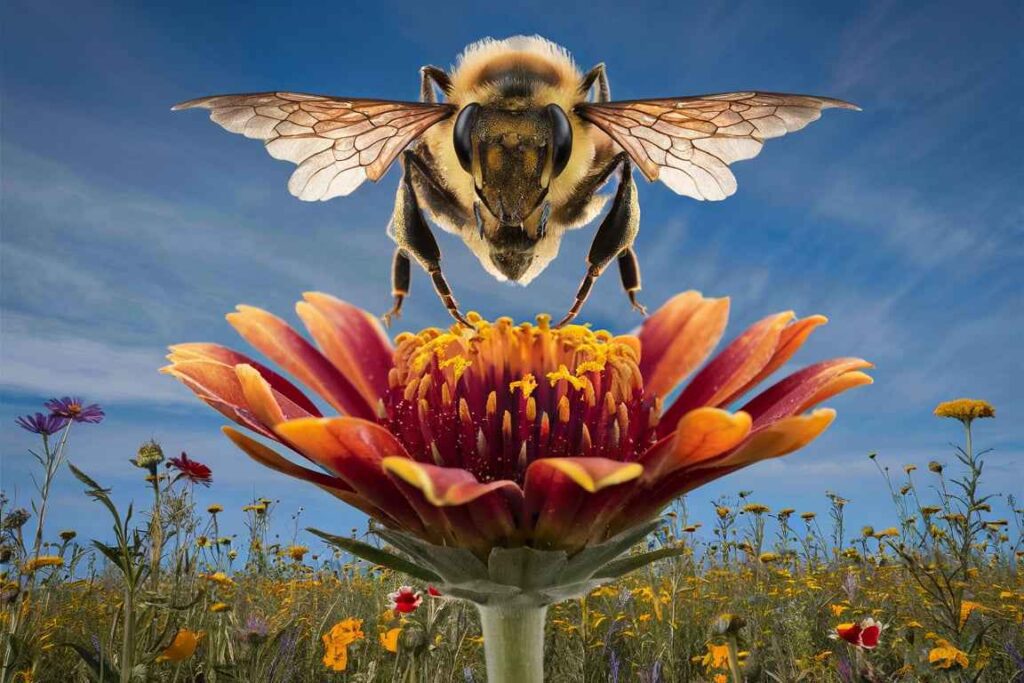

- Biotic agents include insects, birds, bats, and other animals.
- Abiotic agents include wind and water.
Fertilization
After pollination, the pollen grain germinates on the stigma, and a pollen tube develops from the style to the ovary. The pollen tube transports sperm cells to the ovule, where they fertilize and form a zygote.
Seed and fruit development begins after fertilization
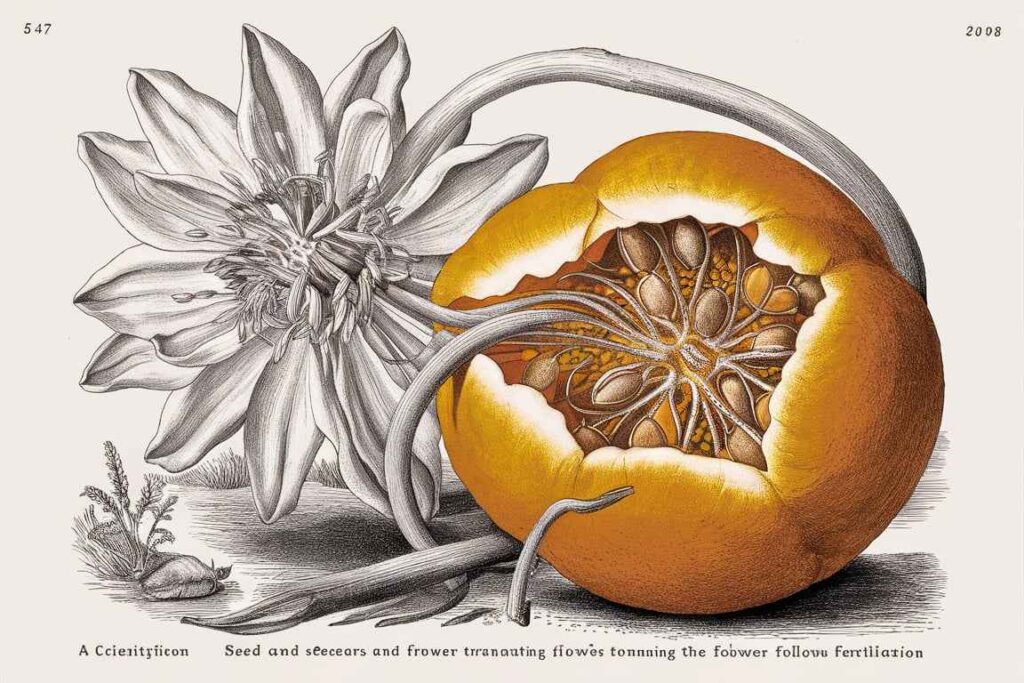
- The zygote grows into an embryo.
- The ovule becomes a seed.
- The ovary develops into a fruit that protects and disperses the seed.
Asexual reproduction in angiosperms
Angiosperms can reproduce asexually by a variety of means, including:
1. Vegetative propagation is the process of producing new plants from vegetative elements such as roots, stems, and leaves. Here are several examples:
- Runners are horizontal stems that grow on the soil’s surface.
- Tubers are swollen underground stems (like potatoes).
- Bulbs are underground storage organs (e.g. onions).
2. Apomixis is the generation of seeds without fertilization in which the seeds are genetically identical to the parent plant.
Specialized Structures and Adaptations
Angiosperms have evolved a variety of specialized structures and adaptations to improve reproductive success, including:
- Nectar Guides: Patterns on petals that lead bees to nectar.
- Self-Incompatibility Mechanisms: Prevent self-fertilization while encouraging cross-pollination for genetic diversity.
- Different Fruit Types: Adapted to varied dispersal mechanisms (e.g., wind-dispersed dandelion seeds and animal-dispersed berries).
Frequently Asked Question
Define Reproduction in Angiosperm
Reproduction in angiosperms, or flowering plants, is the process by which these plants generate offspring to ensure the survival of their species. This procedure can occur in both sexual and asexual ways. Reproduction in angiosperms is the biological process by which flowering plants produce offspring, either through sexual reproduction, which involves the formation and fusion of male and female gametes to produce seeds,
What are the Sexual Reproduction in Angiosperms.
The Sexual Reproduction in Angiosperms are
1. Flower Structure
2. Pollination
3. Fertilization

