Protein synthesis is one of the most fundamental biological processes, responsible for the generation of proteins that perform structural, enzymatic, and regulatory functions in living organisms. This process occurs through two main stages: transcription and translation. While transcription involves the formation of messenger RNA (mRNA) from a DNA template, translation is the decoding of this mRNA sequence into a corresponding polypeptide chain.
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms carry out translation, but significant differences exist between these two systems owing to variations in cellular organization, ribosomal structure, molecular mechanisms, and regulatory controls. This content aims to explain in detail the process of translation in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, while also highlighting the major differences between them.
Summary of Prokaryotic Translation and Eukaryotic Translation
- Prokaryotic translation is coupled with transcription; eukaryotic translation occurs separately in the cytoplasm.
- Prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S; eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S.
- Prokaryotes use N-formylmethionine to start; eukaryotes use methionine.
Table of Contents
Definition of Translation
Translation is the process by which the genetic code carried by messenger RNA (mRNA) is read by ribosomes to produce a specific sequence of amino acids, forming a polypeptide chain or protein. This process occurs within the cytoplasm in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and involves the participation of ribosomes, transfer RNA (tRNA), and various enzymes and factors.
Overview of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Before comparing translation processes, it is essential to understand the basic distinctions between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria and archaea, lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. In contrast, eukaryotic cells, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, possess a well-defined nucleus and various membrane-bound organelles.
This fundamental difference in cellular structure influences the location, timing, and mechanisms of translation in these two systems.
Site of Translation
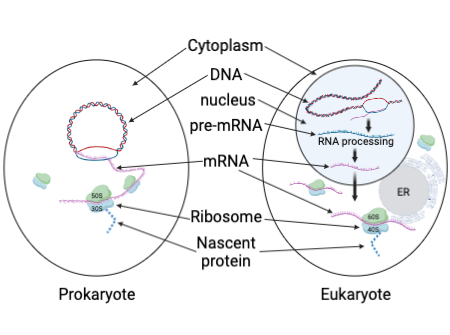
In prokaryotic cells, translation occurs directly in the cytoplasm as there is no nucleus to separate the genetic material from the ribosomes. As soon as an mRNA molecule is transcribed from DNA, ribosomes immediately attach to it and begin translation, often while transcription is still ongoing.
In contrast, eukaryotic translation takes place in the cytoplasm, but transcription occurs inside the nucleus. The mRNA produced through transcription must undergo processing (such as capping, polyadenylation, and splicing) before it is transported through nuclear pores into the cytoplasm, where ribosomes initiate translation. This separation of transcription and translation is a distinctive feature of eukaryotic cells.
Nature of mRNA
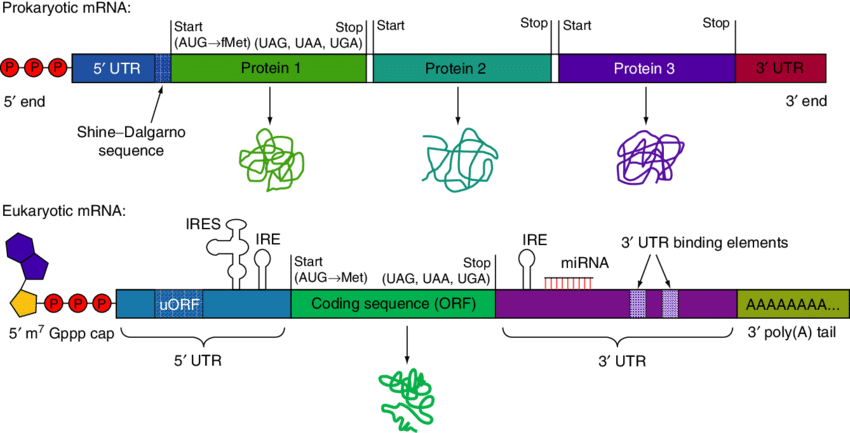
Prokaryotic mRNA is typically polycistronic, meaning a single mRNA molecule may contain multiple coding sequences or open reading frames (ORFs). This allows a single prokaryotic mRNA to encode several different proteins, often part of the same metabolic pathway, organized as an operon.
Eukaryotic mRNA, however, is generally monocistronic. Each mRNA molecule usually carries the information to synthesize only one type of protein. Additionally, eukaryotic mRNA undergoes extensive post-transcriptional modifications, including the addition of a 5’ methylguanosine cap, a 3’ poly-A tail, and removal of introns through splicing, processes that are absent in prokaryotic cells.
Ribosome Structure
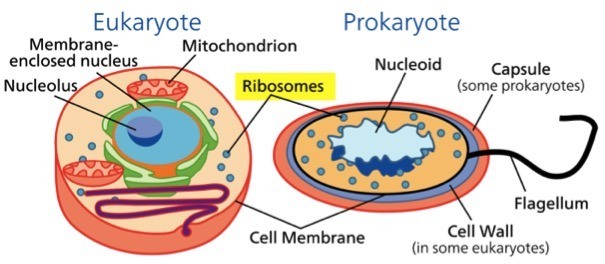
The ribosomes in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in size, composition, and sedimentation coefficient. Prokaryotic ribosomes are smaller, having a sedimentation coefficient of 70S, composed of a 50S large subunit and a 30S small subunit.
Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger, with a sedimentation coefficient of 80S, consisting of a 60S large subunit and a 40S small subunit. The structural differences in ribosomes not only influence the assembly of the translation machinery but also make them targets for selective antibiotics that inhibit prokaryotic translation without affecting eukaryotic ribosomes.
Initiation of Translation
The initiation of translation begins with the assembly of the ribosomal subunits, mRNA, and initiator tRNA at the start codon. In prokaryotes, the initiation complex forms directly at the Shine-Dalgarno sequence, a purine-rich sequence on the mRNA that pairs with a complementary sequence on the 16S rRNA of the 30S subunit. This alignment positions the start codon (usually AUG) appropriately in the ribosomal P-site.
In eukaryotic cells, the process is more complex. The small 40S subunit, along with several initiation factors and the initiator methionyl-tRNA (tRNAi^Met), first binds to the 5’ cap of the mRNA. The complex then scans the mRNA in a 5’ to 3’ direction until it encounters the first AUG codon located within a favorable Kozak sequence. The large 60S subunit then joins the complex to form a functional 80S ribosome.
Initiator tRNA and First Amino Acid
In prokaryotic translation, the initiator tRNA carries a modified form of methionine known as N-formylmethionine (fMet). This modification facilitates recognition by the initiation complex and assists in the initiation of protein synthesis.
In eukaryotes, the initiator tRNA carries a normal methionine (Met) without formylation. Despite this difference, both systems utilize a specialized initiator tRNA distinct from those used during the elongation phase.
Number and Role of Initiation Factors
Prokaryotic translation requires three primary initiation factors: IF-1, IF-2, and IF-3. These factors assist in the assembly of the initiation complex, stabilization of the mRNA-ribosome interaction, and recruitment of the initiator tRNA.
In contrast, eukaryotic translation involves more than ten initiation factors, collectively referred to as eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs). These include eIF1, eIF2, eIF3, eIF4F complex (which comprises eIF4A, eIF4E, and eIF4G), and others. The eIFs participate in functions such as cap recognition, mRNA scanning, ribosomal subunit joining, and regulation of translation under different cellular conditions.
Elongation Process
The elongation stage of translation, involving the sequential addition of amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain, occurs through similar mechanisms in both systems but employs different elongation factors.
In prokaryotes, the elongation process involves elongation factors EF-Tu, EF-Ts, and EF-G. EF-Tu escorts aminoacyl-tRNAs to the ribosome, EF-Ts regenerates EF-Tu, and EF-G facilitates the translocation of the ribosome along the mRNA.
Eukaryotic elongation involves elongation factors such as eEF1α, eEF1βγ, and eEF2. eEF1α performs a role analogous to EF-Tu, while eEF2 is responsible for ribosomal translocation.
Termination of Translation
Termination occurs when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered in the mRNA. In prokaryotic cells, this process involves release factors RF-1, RF-2, and RF-3. RF-1 recognizes UAA and UAG, RF-2 recognizes UAA and UGA, and RF-3 facilitates the release of the polypeptide chain and disassembly of the ribosomal complex.
In eukaryotes, a single release factor, eRF1, recognizes all three stop codons. eRF3, a GTP-binding protein, assists in releasing the newly synthesized polypeptide chain and dissociating the translation machinery.
Post-Translational Modifications
Prokaryotic proteins typically undergo fewer and simpler post-translational modifications compared to their eukaryotic counterparts. Some common modifications in prokaryotes include removal of the formyl group from the initiating methionine and occasional proteolytic cleavage.
Eukaryotic proteins often undergo extensive post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, methylation, acetylation, and the formation of disulfide bonds. These modifications are essential for proper folding, stability, activation, and cellular localization of the proteins.
Coupling of Transcription and Translation
A unique feature of prokaryotic cells is the coupling of transcription and translation. As there is no nuclear envelope, ribosomes can attach to the mRNA and begin translation even before transcription is completed.
In eukaryotic cells, transcription and translation are separated both spatially and temporally. Transcription occurs inside the nucleus, and the mRNA must be processed and exported to the cytoplasm before translation can begin.
Speed and Efficiency
The rate of translation and its overall efficiency differ significantly between prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems, largely due to cellular organization and ribosomal structure.
Prokaryotic Translation Speed
Prokaryotic translation is generally faster and more efficient. The absence of compartmentalization allows immediate ribosome binding to nascent mRNA transcripts. Additionally, prokaryotic mRNA molecules often encode multiple proteins (polycistronic mRNA), enabling the simultaneous production of several proteins from a single mRNA strand.
The translation rate in prokaryotes is estimated at ~20 amino acids per second, facilitated by the streamlined ribosomal structure and reduced number of regulatory steps.
Eukaryotic Translation Speed
Eukaryotic translation is comparatively slower due to additional regulatory mechanisms and compartmentalization. The need for mRNA processing, transport, and scanning by ribosomes before translation initiation adds complexity and time to the process.
The average rate of eukaryotic translation is ~5-10 amino acids per second. Although slower, this regulated system allows for greater control of gene expression, quality control through mRNA surveillance mechanisms, and diverse post-translational modifications.
Antibiotic Sensitivity
One of the most clinically significant differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic translation lies in their differential sensitivity to antibiotics. Many antibiotics selectively target bacterial ribosomes without affecting eukaryotic ribosomes, owing to their distinct structural differences.
Prokaryotic Translation and Antibiotic Sensitivity
Several antibiotics inhibit prokaryotic translation by binding to the 70S ribosome or its subunits, interfering with different stages of protein synthesis. Examples include:
- Streptomycin: Binds to the 30S subunit, causing misreading of mRNA and inhibition of initiation.
- Tetracycline: Prevents the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA to the ribosomal A site.
- Chloramphenicol: Inhibits peptidyl transferase activity in the 50S subunit.
- Erythromycin: Blocks the exit tunnel of the ribosome, preventing elongation of the peptide chain.
These antibiotics are highly effective against bacterial infections because they do not affect the structurally distinct 80S ribosomes of eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic Translation and Antibiotic Sensitivity
Eukaryotic translation is generally resistant to antibiotics that target prokaryotic ribosomes. However, certain toxins and specific drugs can inhibit eukaryotic protein synthesis. Examples include:
- Cycloheximide: Inhibits peptidyl transferase activity in the 60S subunit.
- Diphtheria toxin: Inactivates elongation factor eEF-2, preventing translocation during elongation.
- Ricin: Removes an adenine base from the 28S rRNA of the 60S subunit, halting translation.
Interestingly, the 70S ribosomes of mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells are sensitive to prokaryotic-targeted antibiotics, reflecting their endosymbiotic bacterial origins.
Conclusion
Although the fundamental principles of translation are conserved across prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, several critical differences exist in their mechanisms due to variations in cellular architecture and complexity. Differences in ribosome structure, initiation factors, initiator tRNA, initiation sequences, and the nature of mRNA contribute to the unique characteristics of translation in these two systems.
Understanding these differences is essential not only for comprehending the molecular basis of protein synthesis but also for developing antibiotics and therapeutic agents that can selectively target prokaryotic translation without affecting eukaryotic cells. The study of translation mechanisms in both systems continues to reveal insights into cellular function, gene regulation, and the evolutionary relationship between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic translation?
Prokaryotic translation occurs simultaneously with transcription in the cytoplasm, uses 70S ribosomes, and starts with N-formylmethionine. Eukaryotic translation is separate from transcription, uses 80S ribosomes, and begins with methionine
How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic translation similar?
Both use mRNA, ribosomes, tRNA, and follow the same basic steps: initiation, elongation, and termination to synthesize proteins.
What is the process of translation in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Translation starts when ribosomes bind to mRNA, reads codons to match amino acids via tRNA, forms a growing polypeptide chain, and ends at a stop codon to release the protein.