Microbial chitinases are valuable enzymes produced through optimized fermentation processes involving the selection of efficient microorganisms, culture condition optimization, and advanced purification techniques. Their applications span agriculture, waste management, medicine, food, and biotechnology, making them crucial for sustainable and innovative solutions in various industries.
Table of Contents
Microbial chitinase
Microbial Chitinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of chitin, a major structural component in the exoskeletons of arthropods and the cell walls of fungi. Microbial chitinases, produced by bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes, play an essential role in nature by recycling chitin. They have various industrial and biotechnological applications due to their ability to degrade chitin.
Production Process for Microbial Chitinase
Microbial chitinase synthesis consists of numerous phases, including microbe selection, culture condition optimization, fermentation, enzyme extraction, and purification.
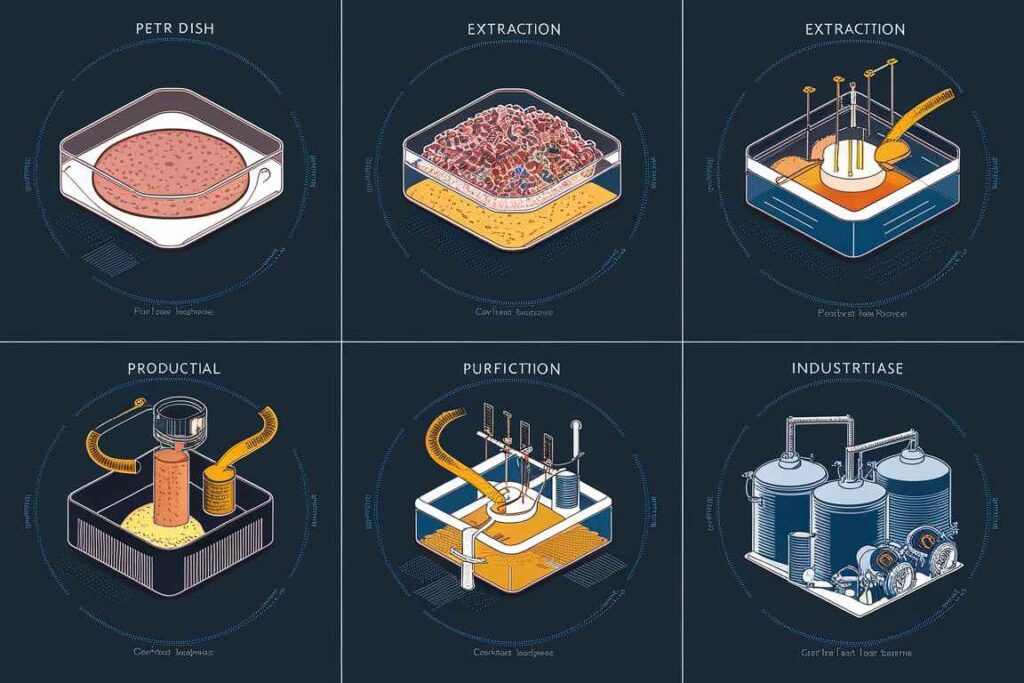
Selection of microorganisms
Isolation: Chitinase-producing microorganisms are isolated from natural sources such as soil, marine environments, and organic waste.
Screening: Strains are tested for chitinase synthesis with chitin-containing medium and detection methods such as clear zone development around colonies on chitin agar plates.
Optimizing Cultural Conditions
Chitin (crab or shrimp shells, pure chitin) serves as the major substrate for enzyme induction.
Carbon and Nitrogen Sources: The medium’s composition, including carbon and nitrogen sources, is tuned to maximize enzyme synthesis.
Environmental factors include pH, temperature, aeration, and agitation speed, which are tuned to maximize chitinase yield.
Fermentation
In batch fermentation, microorganisms are cultivated with all nutrients provided at the start and chitinase synthesis monitored throughout time.
Fed-Batch Fermentation: Nutrients are provided at regular intervals to support microbial development and extend the production phase.
Continuous Fermentation: Fresh medium is continuously given, and culture broth is withdrawn at a consistent rate to maintain steady-state conditions for long-term enzyme synthesis.
Enzyme Extraction
Cell Lysis: To liberate intracellular chitinase, cells are lysed either physically (sonication, homogenization) or chemically (lysozyme, detergents).
Filtration and centrifugation: The culture broth is filtered and centrifuged to eliminate cell debris, resulting in a crude enzyme extract.
Enzyme Purification
Ammonium sulfate precipitation is a method for concentrating and partially purifying chitinase.
Chromatography: Ion-exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography, and affinity chromatography are used to reach better purity levels.
Dialysis is the process by which salts and other small molecules are removed from an enzyme solution.
Applications of Microbial Chitinase
Microbial chitinases’ capacity to digest chitin makes them useful in a variety of sectors.
Agriculture:
Chitinases are employed as biopesticides to combat fungal diseases and nematodes in crops by breaking down their chitinous cell walls.
Plant development Promotion: They improve plant development by lowering the prevalence of fungal infections and encouraging beneficial microbial interactions.
Waste Management:
- Chitinases can transform chitinous waste from seafood processing into valuable products like chitooligosaccharides and N-acetylglucosamine.
- Biodegradation: They play a role in the biodegradation of chitin-containing materials in the environment.
Medical and Pharmaceutical Industry
Chitinases are being investigated as antifungal medicines to treat fungal infections in the medical and pharmaceutical industries.
Chitosan and its derivatives, which are formed by chitinase activity, are employed in drug delivery systems because they are biocompatible and biodegradable.
Food and Feed Industry
Food Additives: Chitooligosaccharides generated by chitinase are used as food additives having prebiotic and preservation qualities.
Animal Feed: Chitinase-treated chitin can be used as a feed supplement to help animals’ gastrointestinal health and nutrient absorption
Biotechnology
DNA Extraction: Chitinases degrade chitinous cell walls to extract DNA from fungal and insect tissues.
Chitinases are proteins that have been engineered to improve their stability and activity for use in industry.
Frequently Asked Question
What is Microbial chitinases ?
Microbial Chitinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of chitin, a major structural component in the exoskeletons of arthropods and the cell walls of fungi. Microbial chitinases, produced by bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes, play an essential role in nature by recycling chitin.
What are the application of Microbial Chitinase ?
The application of applications of Microbial Chitinase are
1. Agriculture
2. Waste Management
3. Medical and Pharmaceutical Industry
4. Biotechnology
Related Article

