Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) is a fundamental concept in population genetics that describes the genetic variation in a population under certain conditions. It provides a mathematical model to study the genetic makeup of a population and to understand the forces that can cause changes in allele frequencies over time.
Table of Contents
What is Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium ?
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) is a fundamental notion in population genetics that explains a population’s genetic makeup in the absence of evolution. It states that in the absence of evolutionary forces, allele and genotype frequencies in a population will be stable from generation to generation. This equilibrium serves as a baseline against which to compare observed genetic data, allowing researchers to determine whether and how populations evolve.
Conditions of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
To be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, a population must satisfy the following five conditions:
- Large Population Size: The population must be sufficiently enough to reduce random changes in allele frequencies (genetic drift).
- No Mutation: There are no mutations that affect allele frequencies.
- No Migration: Individuals do not move into or out of the population.
- Individuals in the population mate randomly based on their genetics.
- No Natural Selection: All genotypes have equal probability of survival and reproduction, implying that no selective pressures favor specific alleles.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
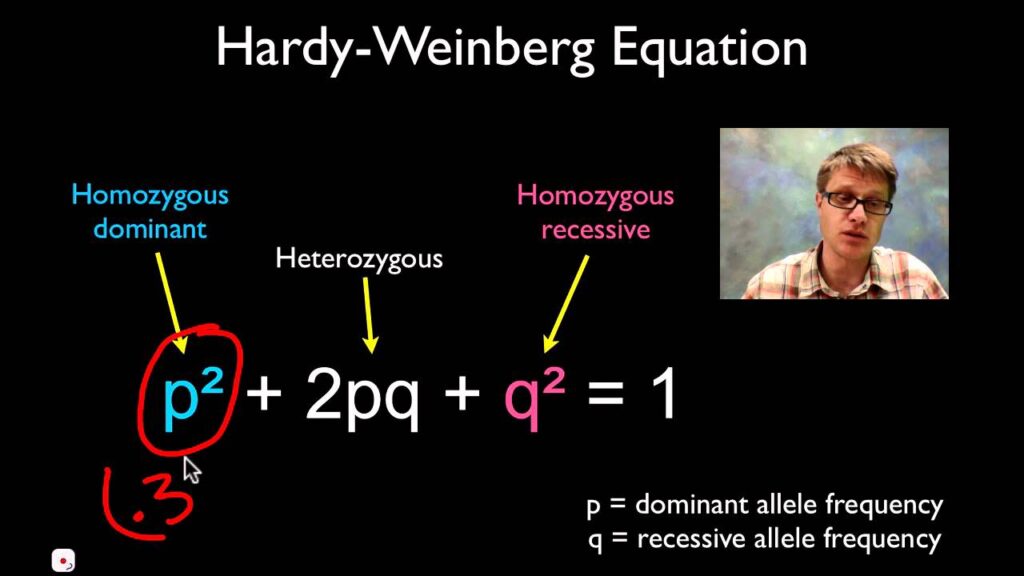
The principle uses two primary alleles at a single gene locus to predict the frequency of genotypes. Let’s denote:
- p as the frequency of one allele (A).
- q as the frequency of the other allele (a).
Since there are only two alleles, their frequencies sum to 1:
p+q=1
The expected genotype frequencies in the population can be calculated using:
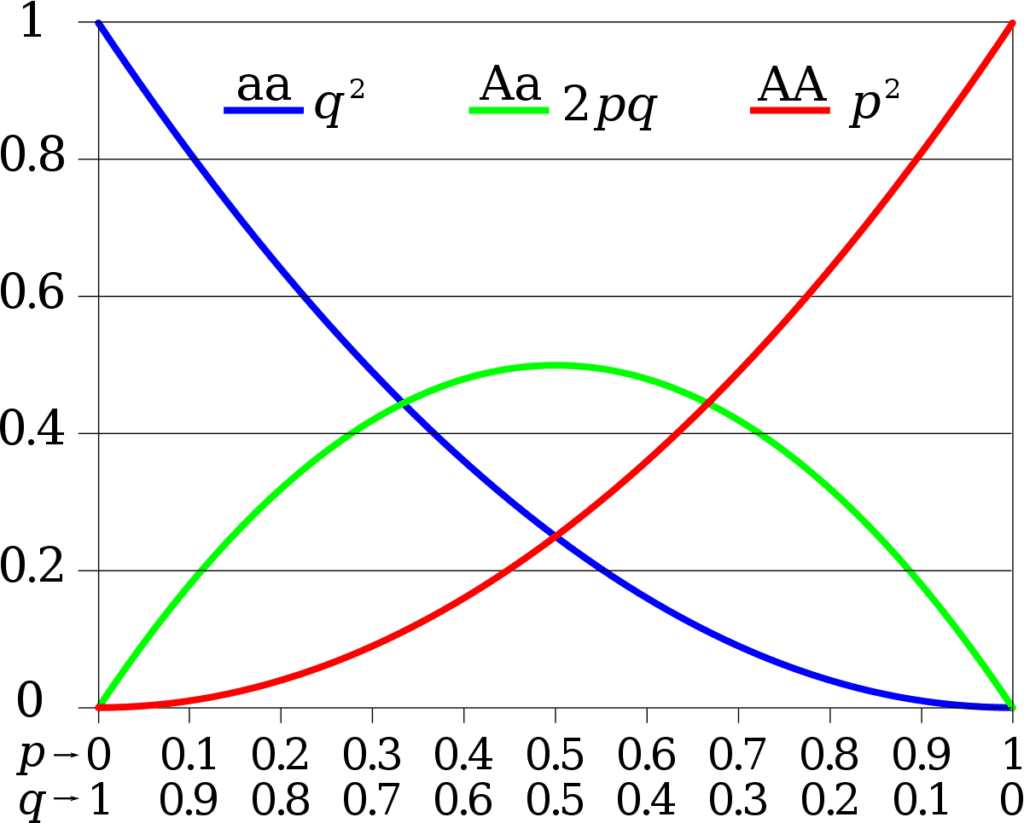
- p2 for the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype (AA).
- 2pq for the frequency of the heterozygous genotype (Aa).
- q2for the frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype (aa).
Therefore, the equation representing the equilibrium is: p2+2pq+q2=1
Example Calculation
Imagine a population where the frequency of allele A (p) is 0.6 and the frequency of allele a (q) is 0.4.
1. Calculate the expected genotype frequencies:
Frequency of AA: p2=0.62=0.36
Frequency of Aa: 2pq=2×0.6×0.4=0.48
Frequency of aa: q2=0.42=0.16
2. Check the sum of the frequencies:
0.36+0.48+0.16=10.36 + 0.48 + 0.16 = 10.36+0.48+0.16=1
Deviations from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
When observed genetic data differs from Hardy-Weinberg expectations, it indicates that one or more of the equilibrium requirements are not met. Possible sources of variances are:
- Genetic drift: Random changes in allele frequencies can occur, particularly in small populations.
- Mutation introduces new alleles, which alter allele frequencies.
- Gene flow occurs when individuals migrate into or out of the population, introducing new alleles or removing existing ones.
- Non-random Mating: If people prefer certain mates based on their genotype, this can affect genotype frequencies.
- Natural selection: Different genotypes’ survival and reproduction rates influence allele frequencies.
Applications of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
- Population Genetics Studies: Offers a theoretical framework for investigating genetic variation and identifying evolutionary causes.
- Evolutionary Biology: Examines changes in allele frequencies to better understand evolution’s causes.
- Forensic Science: Calculates the likelihood of genetic profiles in a population, which aids criminal investigations and identity verification.
- Conservation biology involves monitoring genetic diversity within endangered species populations and developing conservation measures.
Frequently Asked Question
What is Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium ?
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) is a fundamental notion in population genetics that explains a population’s genetic makeup in the absence of evolution. It states that in the absence of evolutionary forces, allele and genotype frequencies in a population will be stable from generation to generation.
What are the applications of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
The applications of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium are
1. Population Genetics Studies
2.Evolutionary Biology
3. Forensic Science
4. Conservation Biology
Related Article

