Ear infections are widespread and can affect several areas of the ear, most notably the external (otitis externa) and middle (otitis media). Here’s an in-depth look at these disorders, including their classifications, causative agents, clinical symptoms, and diagnostic procedures.
Table of Contents
Ear infection
Ear infections are inflammations or infections that can affect any portion of the ear, including the outer ear (external ear), middle ear, or inner ear. The most common ear infections are otitis externa and otitis media
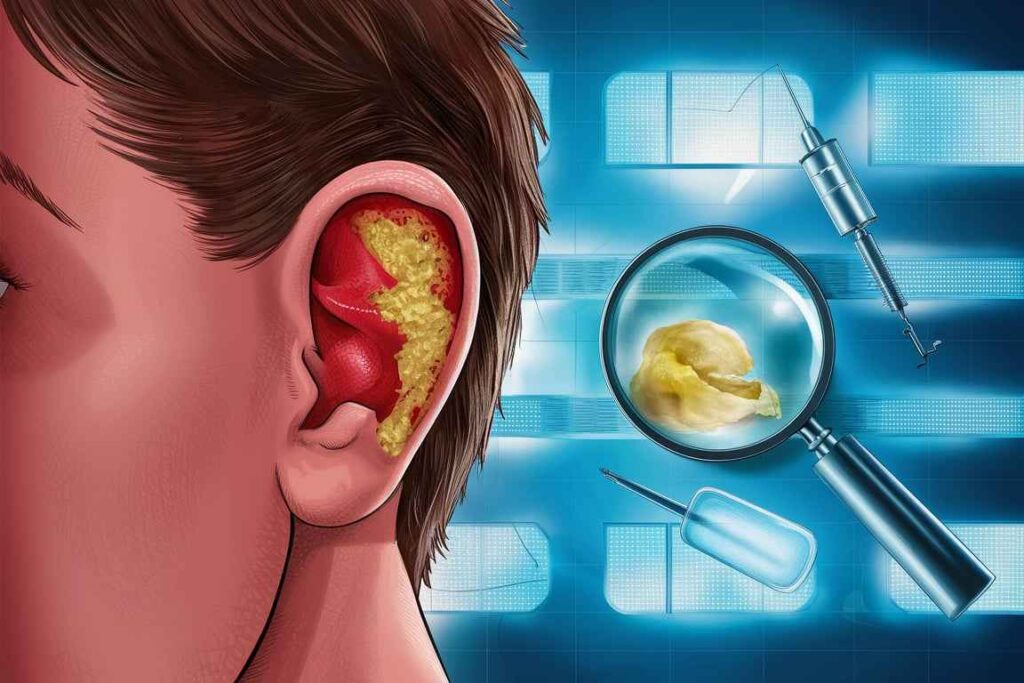
Otitis externa (external )
Types
Acute Otitis Externa (AOE), sometimes known as “swimmer’s ear,” is a sudden onset infection of the ear canal.
Chronic Otitis Externa: An infection that lasts more than six weeks, usually caused by unresolved acute infections or persistent irritants.
Causative agents:
- Bacterial: Pseudomonas aeruginosa (most frequent) and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Fungal infections include Aspergillus and Candida species.
- Herpes zoster oticus (Ramsay Hunt syndrome) is a rare viral condition that can infect the external ear.
Clinical symptoms:
- Pain is usually strong and intensifies with movement of the outer ear.
- Itching: Especially with fungal diseases.
- Discharge might be serous, purulent, or bloody.
- Swelling and Redness in the Ear Canal.
- Hearing loss is temporary and caused by swelling or discharge that blocks the ear canal.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination: A visual inspection using an otoscope to look for symptoms of inflammation, discharge, or ear canal obstruction.
- Culture: Swab ear discharge to detect bacterial or fungal infections.
- Audiometry: To determine if there is a substantial hearing loss.
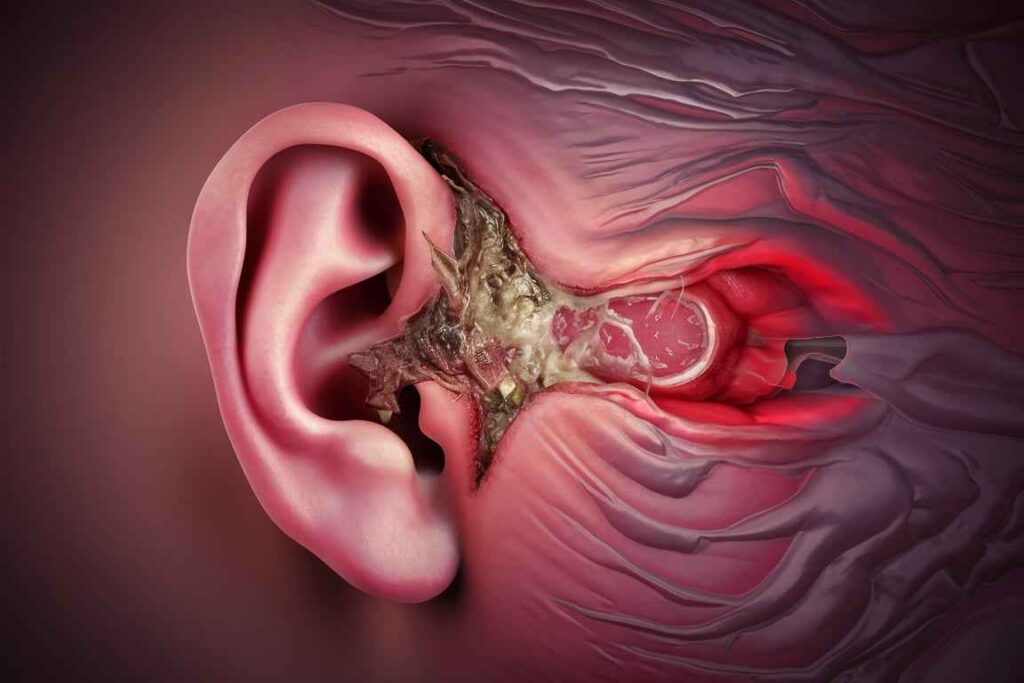
Otitis media (middle ear infection):
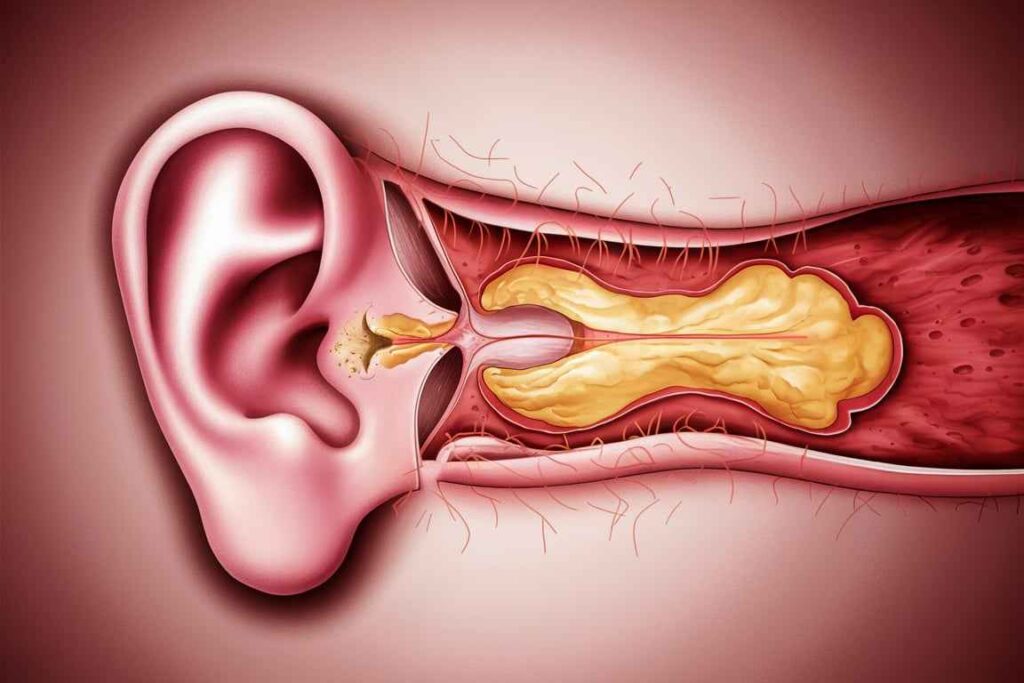
Types
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM) is a rapid-onset illness that is generally accompanied by middle-ear fluid and ear infection symptoms.
- Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) is the presence of non-infected fluid in the middle ear, typically following an episode of AOM.
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) is a persistent ear infection characterized by a perforated tympanic membrane and continuing discharge.
Causative agents:
- Bacteria include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis.
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus, influenza virus, and adenovirus (which frequently precede bacterial illness).
- Fungal infections are uncommon, occurring primarily in immunocompromised individuals.
Clinical symptoms:
- Ear pain is very severe in acute situations.
- Fever is common in AOM.
- Hearing loss is caused by a buildup of fluid in the middle ear.
- Discharge occurs when the tympanic membrane ruptures.
- Tinnitus is a ringing sound in the ear.
- Irritability, particularly in youngsters.
Diagnosis:
- Otoscopy is used to see if the tympanic membrane bulges, is red, or has perforations.
- Tympanometry evaluates middle ear fluid and eustachian tube function.
- Hearing tests use audiometry to determine the level of hearing loss.
- Culture: If there is discharge, a sample can be collected to identify the pathogen.
Comparison and Key Points.
Otitis externa:
- Location: Impacts the ear canal.
- Symptoms include severe discomfort, itching, discharge, redness, and swelling in the ear canal.
- Diagnosis: mostly clinical, with ocular investigation and possibly discharge culture.
- Topical antibiotics or antifungals, analgesics, and ear cleansing are all used as treatment.
Otitis media:
- Affects the middle ear area behind the tympanic membrane.
- Symptoms include ear pain, fever, hearing loss, and potential discharge if the tympanic membrane ruptures.
- Diagnosis: Otoscopy, tympanometry, and hearing testing.
- Treatment includes oral antibiotics for bacterial infections, analgesics, and, in some cases, surgical procedures such as tympanostomy tubes for recurring infections.
Frequently Asked Question
What is Ear infection ?
Ear infections are inflammations or infections that can affect any portion of the ear, including the outer ear (external ear), middle ear, or inner ear. The most common ear infections are otitis externa and otitis media
What are types of otitis media (middle ear infection)?
The types of otitis media (middle ear infection) are:
1. Acute Otitis Media (AOM) is a rapid-onset illness that is generally accompanied by middle-ear fluid and ear infection symptoms.
2. Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) is the presence of non-infected fluid in the middle ear, typically following an episode of AOM.
3. Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) is a persistent ear infection characterized by a perforated tympanic membrane and continuing discharge.
Related Article

