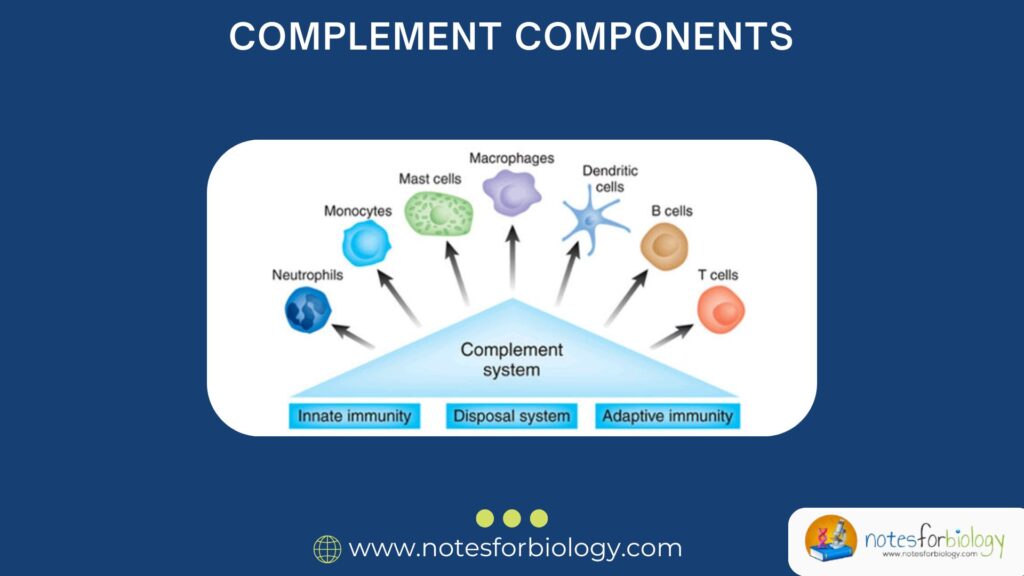
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus (CCHFV)
Introduction Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus (CCHFV) is a deadly virus that causes a severe form of viral hemorrhagic fever in humans. It is one of the most widespread tick-borne viruses known to infect humans and is of great public health concern due to its high fatality rate, potential for outbreaks, and absence of a widely […]