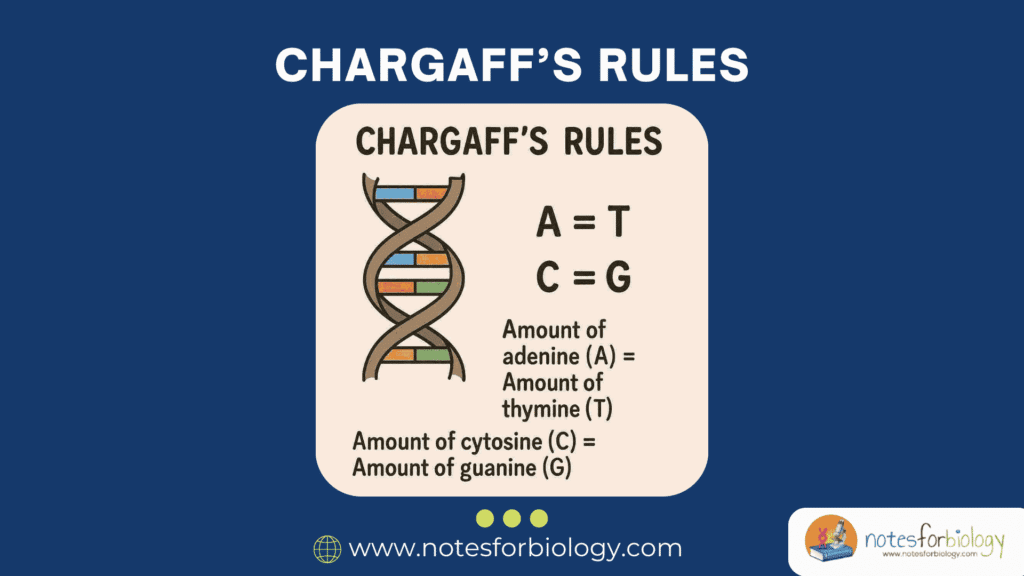
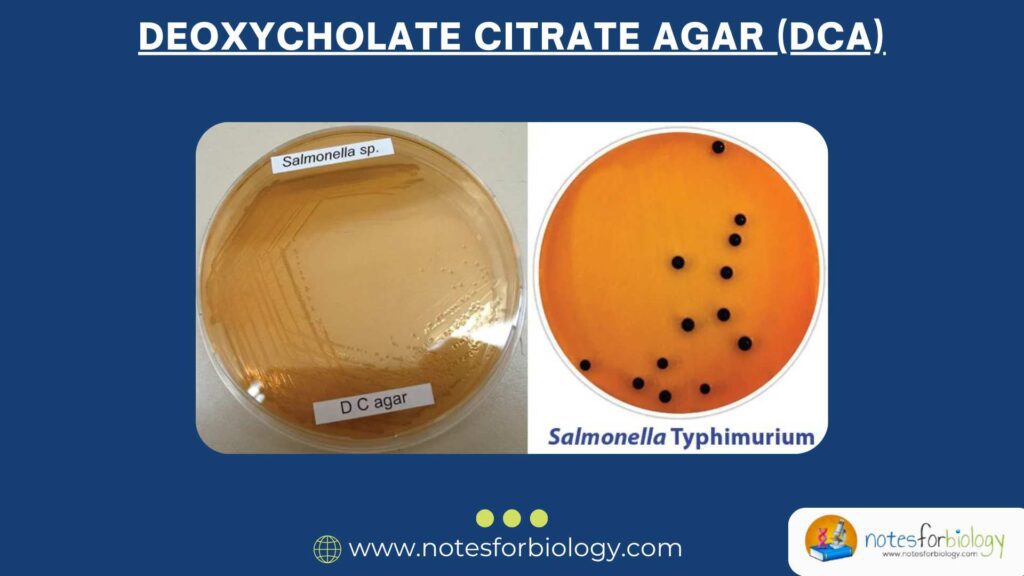
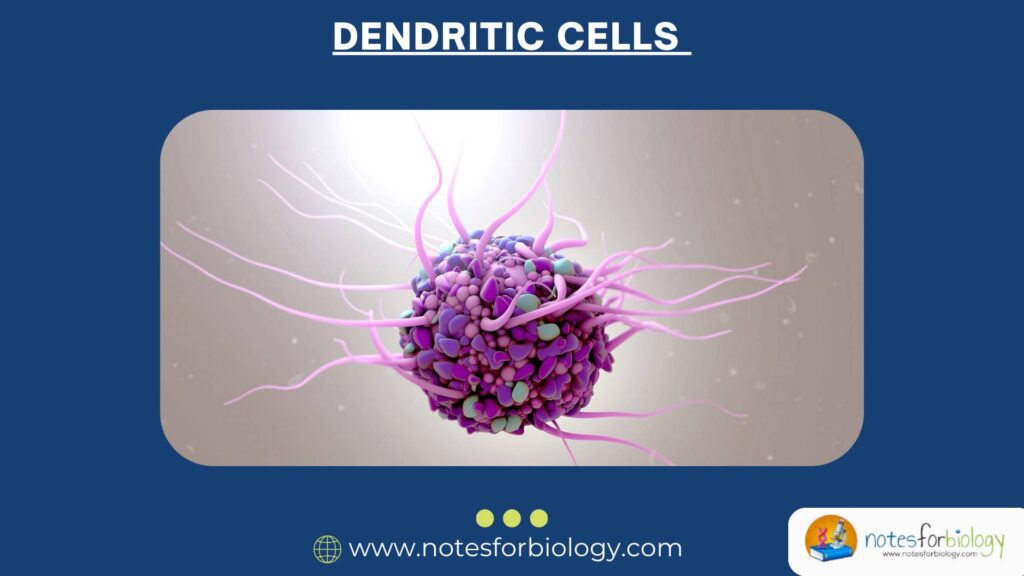
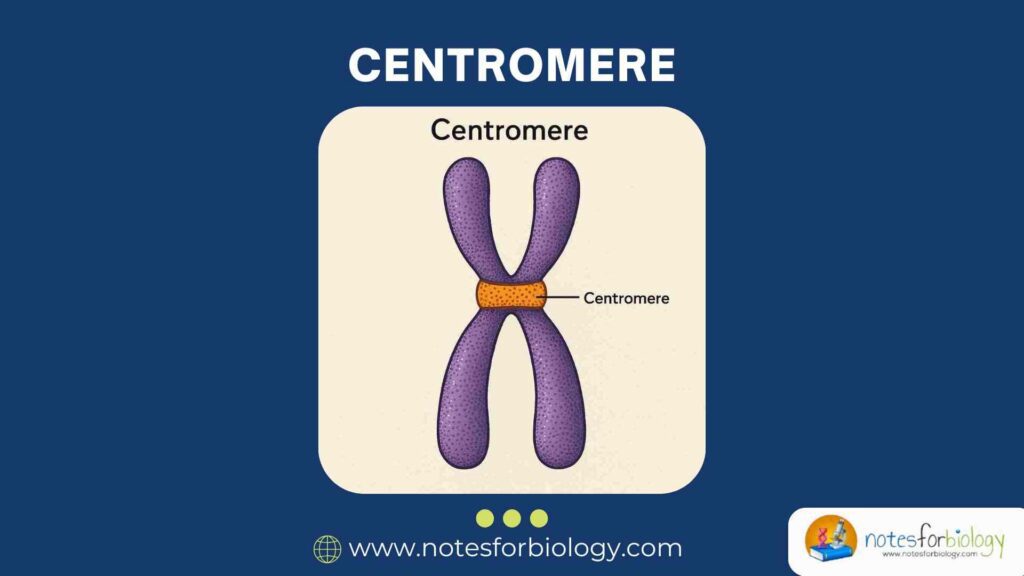
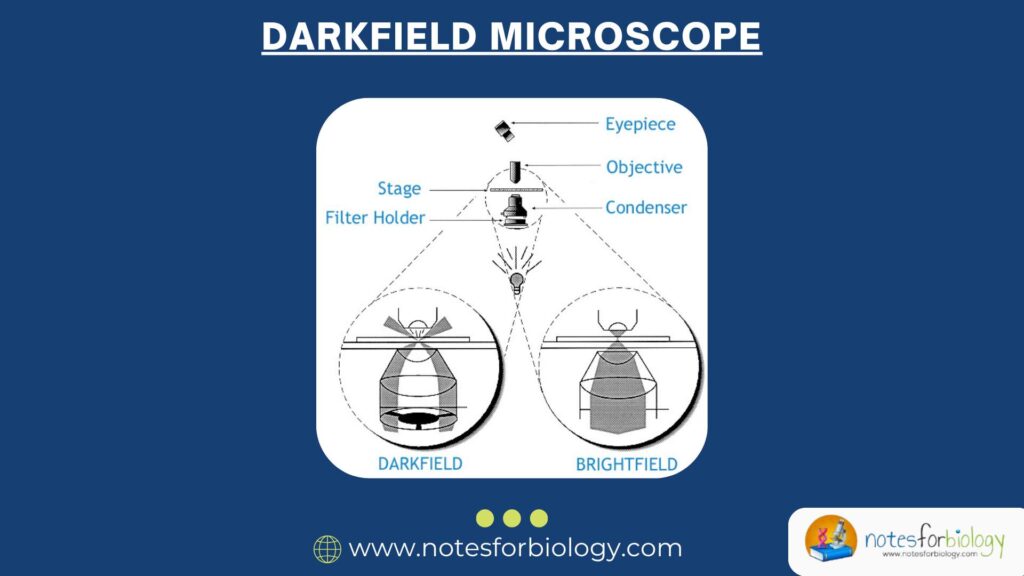
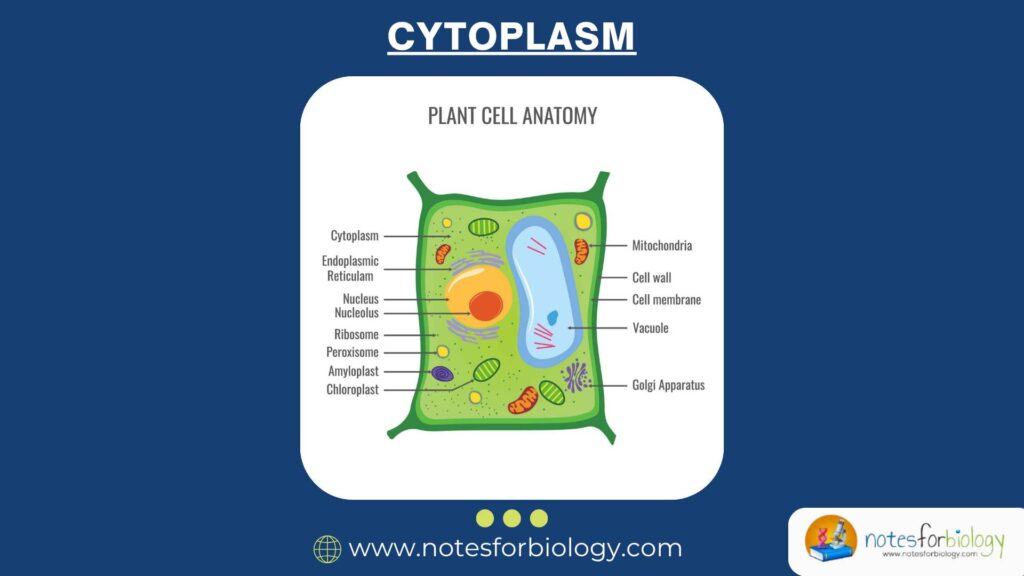
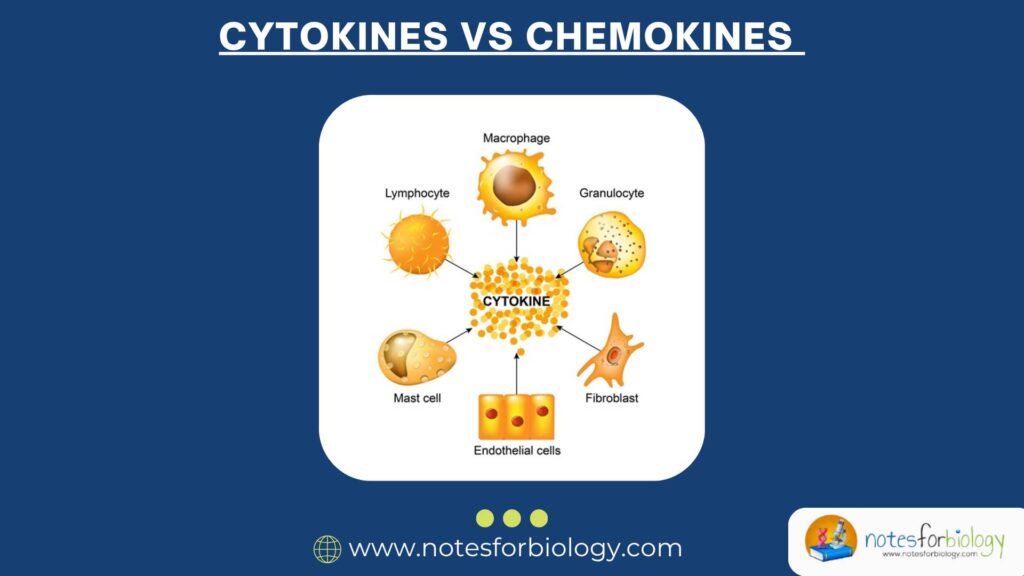
Diarrhea vs Dysentery
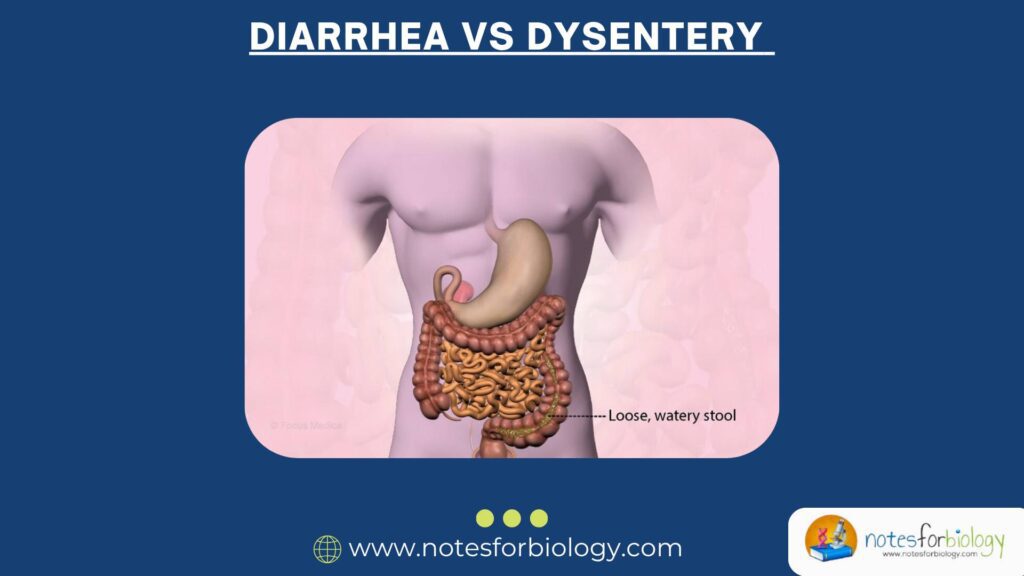
Introduction Diarrhea and dysentery are common gastrointestinal disorders that affect millions of people worldwide, particularly in developing countries. Though both involve frequent and loose bowel movements, they are fundamentally different in terms of causes, symptoms, severity, and treatment approaches. Understanding the differences between these two conditions is essential for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and proper […]