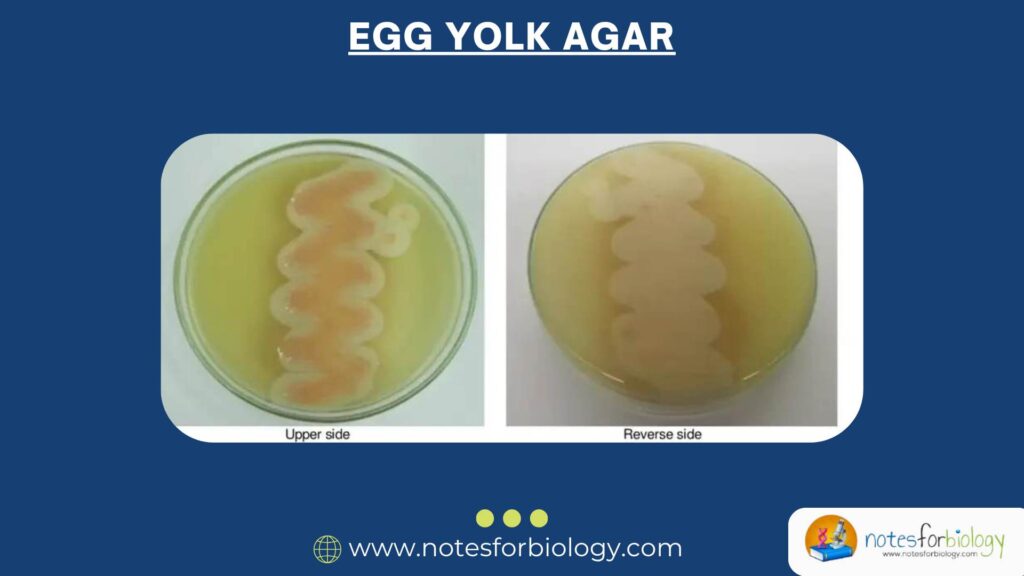
EMB Agar
Introduction Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar is a selective and differential culture medium primarily used for the isolation and differentiation of Gram-negative enteric bacteria, especially coliforms and fecal coliforms like Escherichia coli. This medium serves as a powerful diagnostic tool in microbiology laboratories, water quality testing, and clinical diagnostics. Its unique combination of dyes not […]