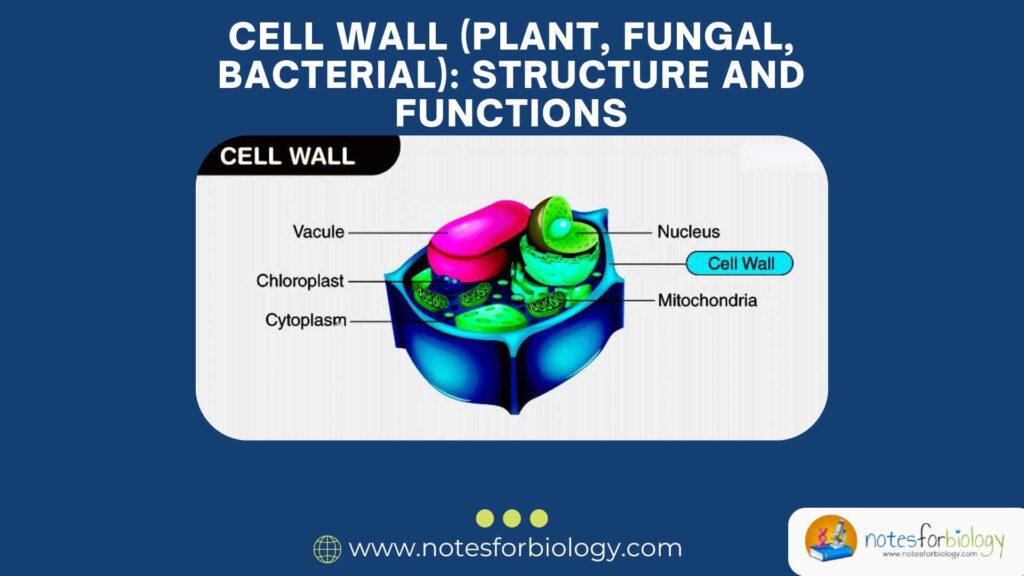
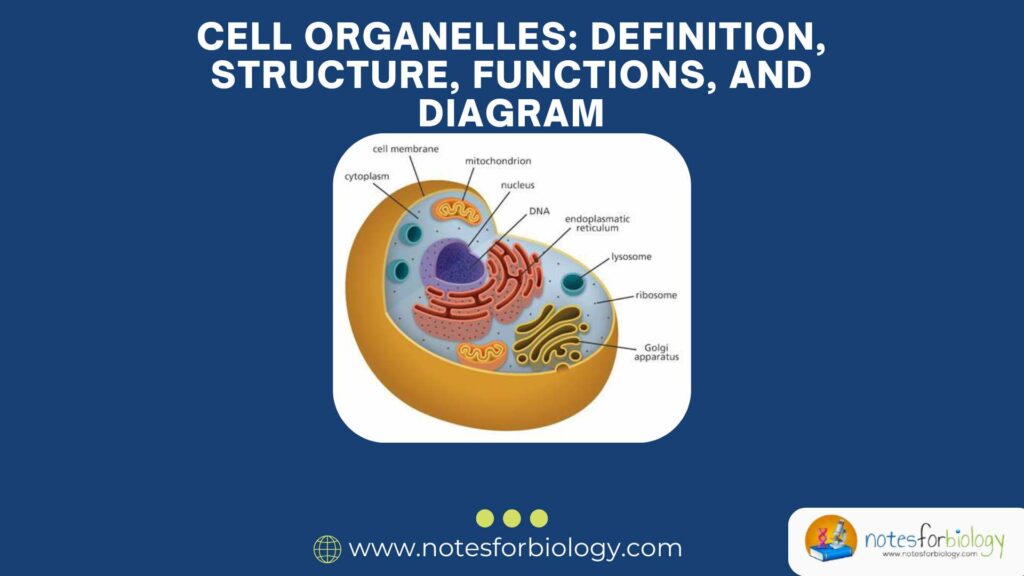
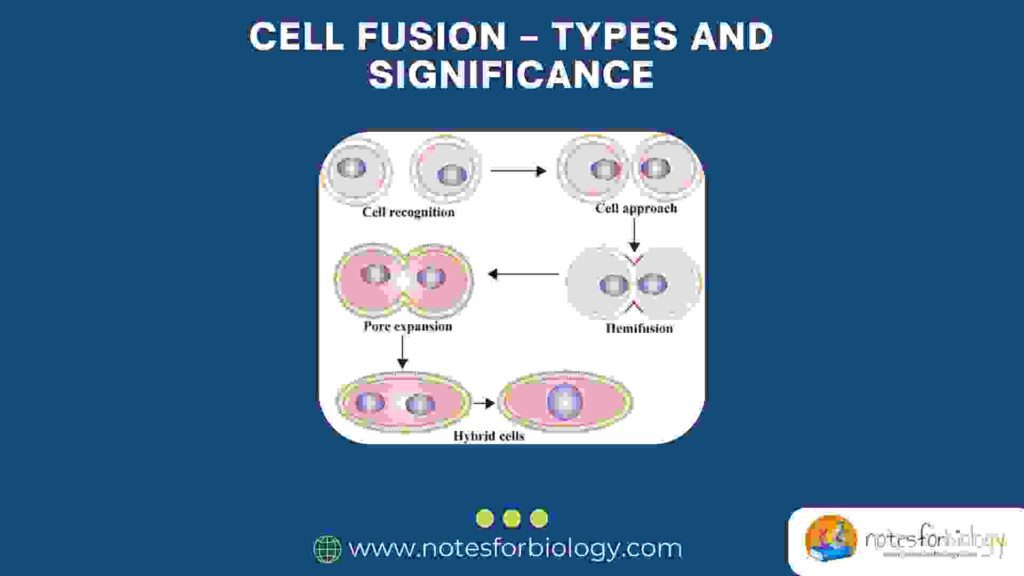
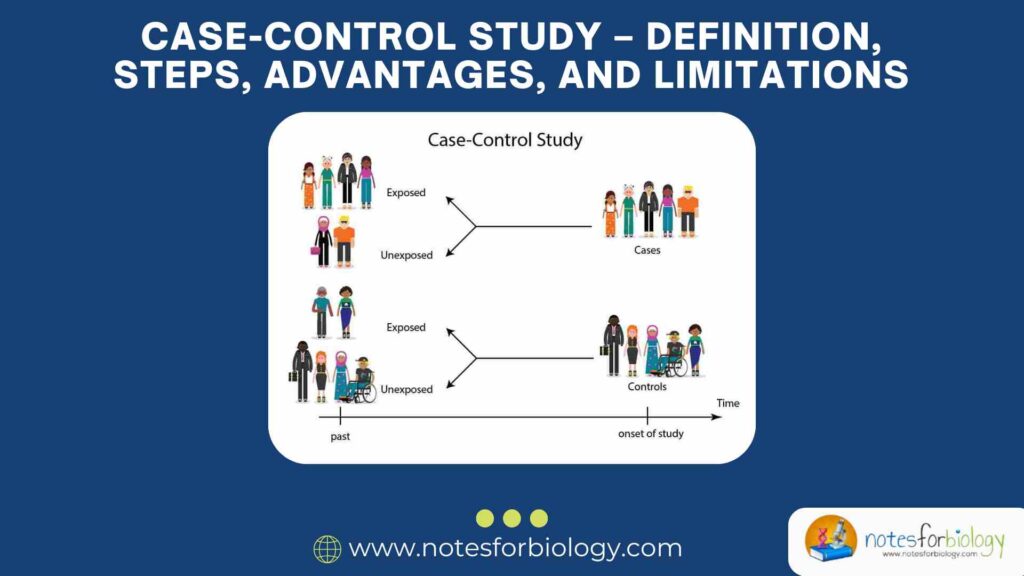
Cellular Respiration
1. Introduction Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells break down glucose in the presence or absence of oxygen to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), along with carbon dioxide and water as by-products. All living organisms need energy to perform their daily functions like moving, growing, repairing damage, and staying alive. This energy comes […]