Factors Of Enzyme Action and Immobilized Enzymes
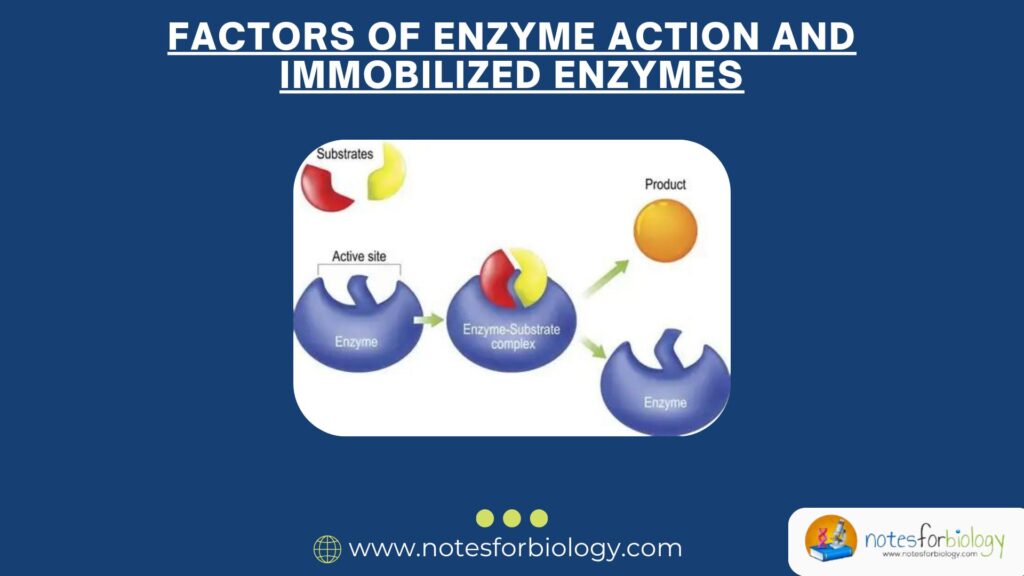
Introduction Enzymes are special proteins that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. They are essential for life because they allow reactions to happen quickly and efficiently, without the need for extremely high temperatures or other harsh conditions. For example, enzymes help digest the food we eat, copy DNA, and make energy inside cells. Without […]
Factors Of Enzyme Action and Immobilized Enzymes Read More »