Butyric Acid Fermentation is an interesting process that is fueled by some bacteria that decompose carbohydrates without oxygen. The main byproduct of this anaerobic process, which is essential to both human and animal digestive systems, is butyric acid. Anaerobic fermentation of butyric acid occurs when specific bacteria break down carbohydrates, like glucose, into butyric acid, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen gas. The Clostridium genus is the main group of obligatory anaerobes that perform this function.
Table of Contents
Principle
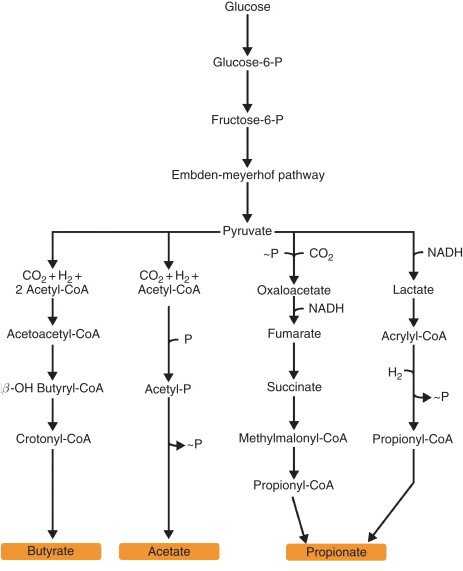
Based on the anaerobic metabolic pathways that some bacteria use to break down carbohydrates, butyric acid fermentation is a theory. These bacteria use glycolysis to break down glucose into pyruvate in the absence of oxygen. Pyruvate is then further broken down into butyric acid by a sequence of metabolic processes. These bacteria benefit from this pathway because it enables them to produce butyric acid and gasses as byproducts and generate energy in oxygen-free situations.
Steps
Glycolysis
- The first step in the process is glycolysis, which turns one glucose molecule (C₆H₁₂O₆) into two pyruvate molecules (C₃H₄O₃), generating a negligible quantity of ATP and reducing equivalents in the form of NADH.
- C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2C₃H₄O₃ + 2ATP + 2NADH
- This phase, which starts in the cytoplasm of the bacterial cell, is where many fermentation pathways begin.
Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA
- Acetyl-CoA is formed when pyruvate is decarboxylated, releasing carbon dioxide (CO₂).
- 2C₃H₄O₃ → 2C₂H₄O-CoA + 2CO₂ is the equation.
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex or related anaerobic bacterial enzyme systems are involved in this step.
Formation of Butyrate (Butyric Acid)
- After going through a number of processes, acetyl-CoA becomes acetoacetyl-CoA, which is then transformed into butyrate. This process involves the synthesis of ATP and a number of intermediates.
- Two C₂H₄O-CoA equals C₄H₇O₂⁻ (butyrate) + CoA + H₂ + CO₂
- The process produces butyric acid in the end and involves enzymes like butyrate kinase and acetoacetic-CoA transferase.
Production of Hydrogen and Carbon Dioxide
- As byproducts of the fermentation process, hydrogen gas (H2) and extra carbon dioxide (CO2) are produced in addition to butyric acid.
- Formula: 4H₃ + 2CO₃
Uses
Industrial Production of Butyric Acid
- Butyric acid is a crucial chemical used in many different industries. It serves as a precursor in the production of artificial flavorings, polymers, and medications. It is useful for making esters and other derivatives due to its special qualities.
Biogas Production
- Biogas can be manufactured by using the hydrogen and carbon dioxide that are created during the fermentation of butyric acid. In sustainable energy programs, this renewable energy source is becoming more and more important.
Food Industry
- Because of its unique flavor and aroma, butyric acid is used as a flavoring agent in the food industry to enhance the flavors of cheeses and other fermented goods. It improves the way different foods feel to the touch.
Animal Feed
- Animal feed contains butyric acid and its derivatives to promote intestinal health and boost nutrition absorption. In particular, this application helps to promote the health and growth of animals.
Probiotics
- Probiotic formulations use specific butyric acid-producing bacteria to maintain the health of the gastrointestinal tract. These probiotics can enhance both human and animal digestive processes and support a balanced, healthy gut flora.
Biodegradable Plastics
- A kind of biodegradable plastic called polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) is made using butyric acid as a precursor. The development of eco-friendly and sustainable materials to lessen plastic pollution depends heavily on this use.
Importance
In the natural world, butyric acid fermentation is essential, especially in animal digestive systems. It helps break down complex carbs and produces short-chain fatty acids, both of which are vital for gut health.
Note: While butyric acid fermentation has numerous benefits, it can also be associated with certain negative aspects, such as the production of undesirable odors and the potential for spoilage in food products.
Conclusion
A basic anaerobic process with a wide range of uses in several industries is butyric acid fermentation. The importance of butyric acid fermentation goes well beyond its metabolic pathway, highlighting its critical role in both industrial processes and ecological sustainability. Applications of butyric acid fermentation include the manufacture of industrial chemicals, contributions to renewable energy, and animal health.
Frequently Asked Question(FAQ)
Define Butyric Acid Fermentation ?
Butyric Acid Fermentation is an interesting process that is fueled by some bacteria that decompose carbohydrates without oxygen.
What are the uses of Butyric Acid Fermentation ?
The synthesis of different butyrate esters, such as methyl butyrate, from butyric acid results in pleasant-tasting and smelling products that are added to food, flavorings, varnishes, medications, and disinfectants.
What is the fermentation process of butyric acid?
Many obligate anaerobic bacteria, primarily from the genus Clostridium, exhibit butyric acid fermentation. These bacteria may convert sugar to pyruvate through the process of glycolysis, as well as occasionally amylose and pectin.
Where is butyric acid Fermentation produced?
At the industrial level, butyric acid is mostly made by chemical synthesis. This is the oxidation of butyraldehyde, which is produced via oxo synthesis from propylene that is taken from crude oil.
Related Article