Buffy Coat is a anticoagulated blood is centrifuged, a concentrated coating of white blood cells and platelets known as the it is created. It is seen as a thin, pale coating that is positioned between the red blood cells and plasma. Because of its high nucleated cell and platelet content, it is essential for many medical and scientific uses, including as genetic analysis, stem cell transplants, infections and hematologic diseases diagnostic tests, and forensic investigations.
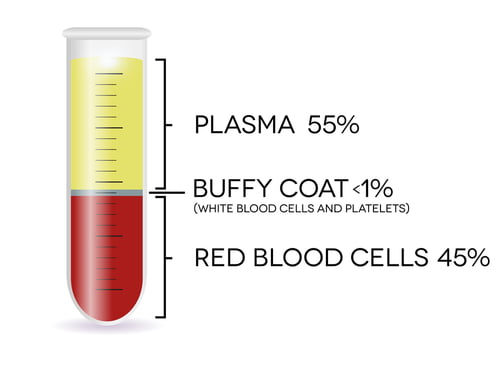
Table of Contents
Definition
It is a thin layer of white blood cells (leukocytes) and platelets that forms when blood is centrifuged. It appears as a pale, yellowish layer between the plasma and red blood cells in a sample of blood that has been treated with an anticoagulant and then centrifuged.
It is a narrow layer of white blood cells and platelets that lies between the red blood cells and plasma in a centrifuged blood sample.
Preparation
1. Blood Gathering
A needle is used to draw blood from a patient or donor, and the blood is then kept in a tube with an anticoagulant (such as citrate or EDTA).
2. Centrifugation
The drawn blood is put into a centrifuge and spun for ten to fifteen minutes at very high speeds (often between 1000 and 2000 g).
Based on their respective densities, the blood components separate due to centrifugal force:
At the top is plasma, which is the least dense material.
A thin intermediate layer is formed by the buffy coat, which is composed of platelets and white blood cells.
The densest cells, red blood cells, sink to the bottom.
3. Buffy Coat Extraction
Following centrifugation, the layers are discernibly divided.
Using a pipette or other specialized tool, It is carefully removed so as not to contaminate the red blood cells and plasma.
Uses
1. Diagnostic Testing
Hematology: White blood cell counts and kinds are assessed by looking at the buffy coat. This helps with immune status monitoring, hematologic problems (including leukemia), infections, and inflammatory diseases.
Microbiology: To find intracellular pathogens like viruses, bacteria, and parasites (like malaria), concentrate white blood cells in the buffy coat.
Molecular biology: Because white blood cells are a rich source of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA are frequently recovered from the buffy coat for genetic testing, PCR, and sequencing.
2. tem Cell and Bone Marrow Transplants
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), which are essential for bone marrow transplants, are found in the buffy coat. HSCs are extracted from the buffy coat and applied to malignancies and other hematopoietic disorders.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
Platelets from They are concentrated to prepare platelet-rich plasma (PRP). PRP is used in regenerative medicine to promote healing in conditions like tendon injuries, osteoarthritis, and for aesthetic treatments.
4. Research
Researchers utilize the buffy coat to look into genetic abnormalities, the immune system, and the development of novel therapies. It offers a concentrated supply of white blood cells for use in research where particular cell populations are needed.
5. Forensic Science
In forensic investigations, DNA from it is utilized to identify people, determine genetic links, and solve crimes.
Conclusion
A vital component in many medicinal, diagnostic, and research applications is the buffy coat. Centrifuging anticoagulated blood to separate it from red blood cells and plasma is the preparation method. it has a strong concentration of white blood cells and platelets, which makes it useful for a variety of medical procedures, therapies, and scientific studies.
Frequently Asked Question
1. What is the use of buffy coat preparation?
Leukocytes from bone marrow or whole blood are concentrated and present in a buffy coat. Large sample quantities can be concentrated and the handling of cell separation downstream can be minimized by creating a buffy coat from whole blood samples.
2. Why is buffy coat used?
Because its include a high concentration of WBCs and platelets, they provide an excellent opportunity to study molecular signals and immune pathways. They are frequently used to harvest DNA from animal blood.
3. What type of parasite is this buffy coat preparation used for?
The best way to observe trypanosoma spp. and microfilaria is to use direct buffy coat smear preparations from the spinning capillary tube (Figures 13-66 and 13-67). These parasites concentrate in the buffy coat.
4. What is the buffy coat production method?
Donations of whole blood are quickly chilled to room temperature on cooling trays at the collection clinic using the buffy coat manufacturing procedure. After blood is collected, platelets from the total blood must be produced within 24 hours. Three separate layers are produced by centrifuging the entire blood.
Related Article