Borescopes are valuable tools in biology for non-invasive internal examinations and observations. They are used in a wide range of fields including veterinary and botanical studies, forensics, and microbial research. However, it’s important to consider limitations such as image quality, accessibility, cost, and potential for damage. Proper training and maintenance are essential to maximize their utility and minimize their drawbacks.
Table of Contents
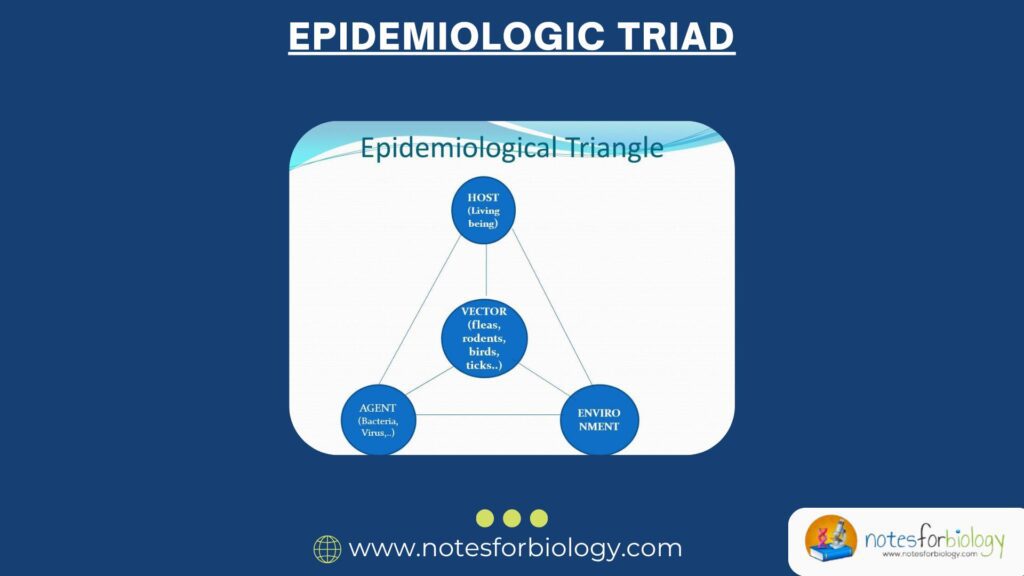
Definition of Borescope in Biology
It, also known as a boroscope, is an optical device that consists of a flexible or rigid tube with an eyepiece on one end and a lens or camera on the other. It is used to visually inspect areas that are difficult to access, such as inside engines, pipes, or other enclosed spaces. In the field of biology, it plays a crucial role in the non-destructive examination of the internal structure of organisms, plant cavities, or other biological specimens. This non-invasive inspection method helps researchers and scientists to study and document the inner workings of living organisms without causing significant harm or requiring extensive dissection.
Uses of Borescope in Biology
- They are non-invasive devices that aid in seeing without causing harm to tissues or organs.
- They are therefore perfect for researching living things.
- They offer incredibly detailed pictures of an organism’s inside.
- This enables researchers to use imaging techniques or the human eye to view details that are unseen to the unaided eye.
- It is possible to place it into long, narrow passageways like the circulatory or digestive systems.
- This makes it possible for researchers to see regions that are inaccessible using conventional imaging methods.
Applications of Borescope
- They are used to view organisms’ internal structures, such as the organs and tissues of animals or plants.
- It helps diagnose and repair biological systems, such as the circulatory or digestive systems.
- It helps to conduct experiments, such as studying the effects of different chemicals on cells or tissues.
- It can be used for teaching and training, like providing students with a close-up view of the internal structures of organisms
Limitations of Borescope in Biology
- This can be expensive, hindering their use in some research settings.
- It can be complex to use, which requires training and expertise.
- It, as the cells lining the digestive tract, can damage delicate tissues.
- This risk should be carefully considered before using it.
Conclusion
They are a valuable tool for biologists. They help in studying organisms’ internal structures, diagnosing and repairing biological systems, conducting experiments, and teaching and training students. They are a new technology and are still evolving. However, they have the potential to revolutionize the way biologists study and understand living organisms. It is important to acknowledge their limitations and use them responsibly.
Frequently Asked Question
What is a borescope?
A borescope is an optical device featuring a flexible or rigid tube with an integrated camera and light source, used for visual inspection of inaccessible areas. In biology, it helps examine the internal structures of organisms, plants, and other biological specimens non-invasively.
How is a borescope used in animal research?
In animal research, they are used for non-invasive internal examinations to diagnose illnesses, monitor internal health, and observe physiological responses and behaviours without the need for surgical procedures.
What are the applications of borescopes in botanical studies?
It is used to explore internal plant structures, such as hollow stems or cavities, to study growth patterns, disease impacts, and internal plant physiology. They are also useful in assessing tree health by inspecting for decay, pests, or disease.
Related Articles