The efficient transport of oxygen by the blood is essential for the survival of all aerobic organisms. Hemoglobin, a specialized protein found in red blood cells, is primarily responsible for binding oxygen in the lungs and releasing it in the tissues where it is needed. However, several physiological factors influence the binding affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. One of the most significant phenomena describing this relationship is the Bohr effect, a vital mechanism that facilitates the unloading of oxygen in metabolically active tissues.
Closely linked with the Bohr effect is the oxygen dissociation curve, which graphically represents the relationship between the partial pressure of oxygen and the percentage saturation of hemoglobin. The curve, along with factors such as carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, and pH, determines how easily hemoglobin binds to or releases oxygen under different conditions.
This content presents a detailed and structured exploration of the Bohr effect, oxygen dissociation curve, and the effects of carbon dioxide, organized under separate subheadings for clarity.
Summary of Bohr Effect
- The Bohr effect describes how increased carbon dioxide levels and lowered pH in tissues reduce hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen, promoting oxygen release where it’s needed most.
- This effect shifts the oxygen dissociation curve to the right, allowing active tissues producing more CO₂ and H⁺ to receive additional oxygen from the blood.
- In the lungs, where CO₂ is expelled and pH is higher, hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen increases, ensuring efficient oxygen uptake.
Table of Contents
Definition of Bohr Effect
The Bohr effect refers to the physiological phenomenon where an increase in carbon dioxide concentration or a decrease in blood pH reduces the oxygen-binding affinity of hemoglobin. In simpler terms, in environments where tissues produce more carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions as a result of high metabolic activity, hemoglobin releases oxygen more readily. Conversely, in areas with lower carbon dioxide levels, such as the lungs, hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen increases, promoting oxygen uptake.
This mechanism was first described by Danish physiologist Christian Bohr in 1904, and it plays a crucial role in ensuring that oxygen is efficiently delivered to tissues that require it the most.
Mechanism of the Bohr Effect
When carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood from actively respiring tissues, it reacts with water to form carbonic acid. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase present in red blood cells. Carbonic acid rapidly dissociates into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻).
The increase in hydrogen ion concentration lowers the pH of the blood. Hemoglobin molecules respond to this acidic environment by reducing their affinity for oxygen. Hydrogen ions bind to specific amino acid residues in hemoglobin, causing a conformational change that favors the release of oxygen.
Similarly, carbon dioxide can directly bind to the amino groups of hemoglobin, forming carbaminohemoglobin. This binding also decreases hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen. Consequently, oxygen is released into the surrounding tissues where it is required for cellular respiration.
Role of Carbonic Acid and pH
Carbonic acid formation plays a pivotal role in the Bohr effect. As carbon dioxide enters red blood cells, it combines with water under the influence of carbonic anhydrase to form carbonic acid. The weak acid then dissociates to release hydrogen ions, leading to a fall in blood pH.
A lower pH affects hemoglobin’s structure, shifting it from the relaxed (R) state, which favors oxygen binding, to the tense (T) state, which favors oxygen release. This shift ensures that in areas of high carbon dioxide concentration and low pH typically metabolically active tissues hemoglobin releases its oxygen load more efficiently.
Thus, the presence of carbonic acid and a resultant decrease in pH are central to the Bohr effect’s functionality.
Formation of Carbaminohemoglobin
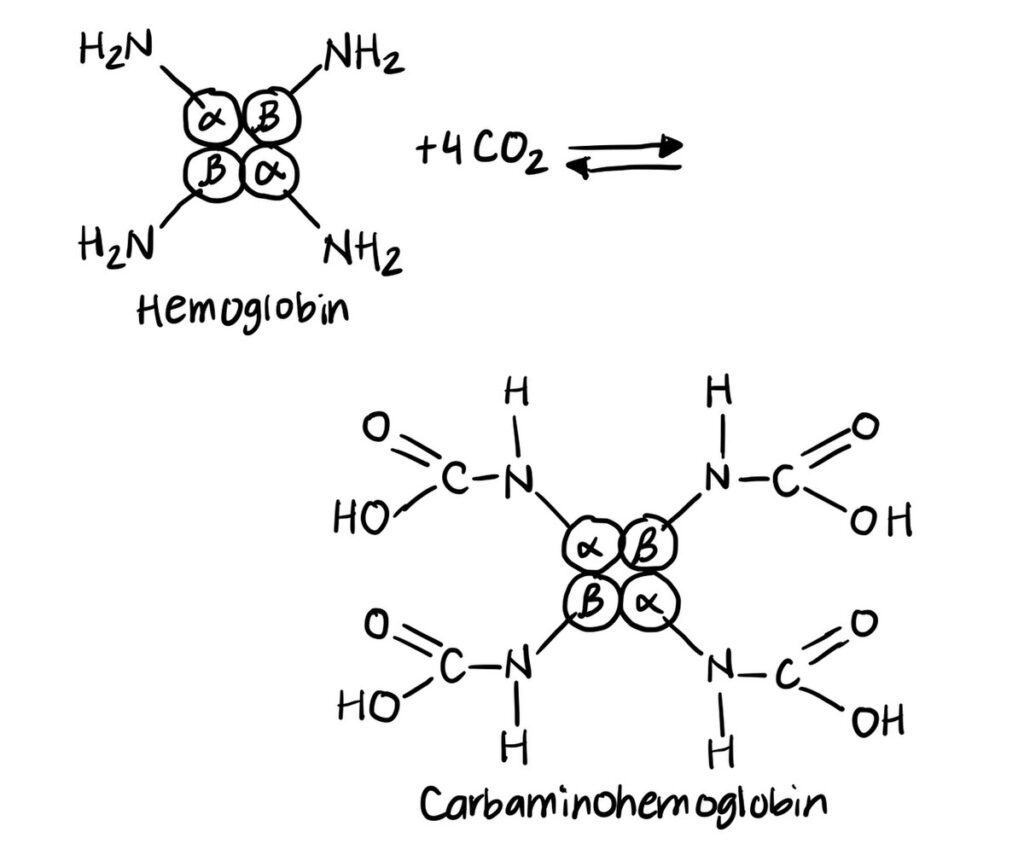
Carbon dioxide also influences oxygen release by directly combining with the amino terminals of hemoglobin polypeptide chains to form carbaminohemoglobin. This compound formation induces a structural alteration in hemoglobin that stabilizes the tense (T) form, reducing its affinity for oxygen.
Approximately 10 to 20 percent of carbon dioxide transported in the blood binds to hemoglobin in this manner. The rest is carried in the form of bicarbonate ions or dissolved in plasma. The formation of carbaminohemoglobin is reversible and facilitates the simultaneous transport of carbon dioxide to the lungs and release of oxygen to the tissues.
The Oxygen Dissociation Curve
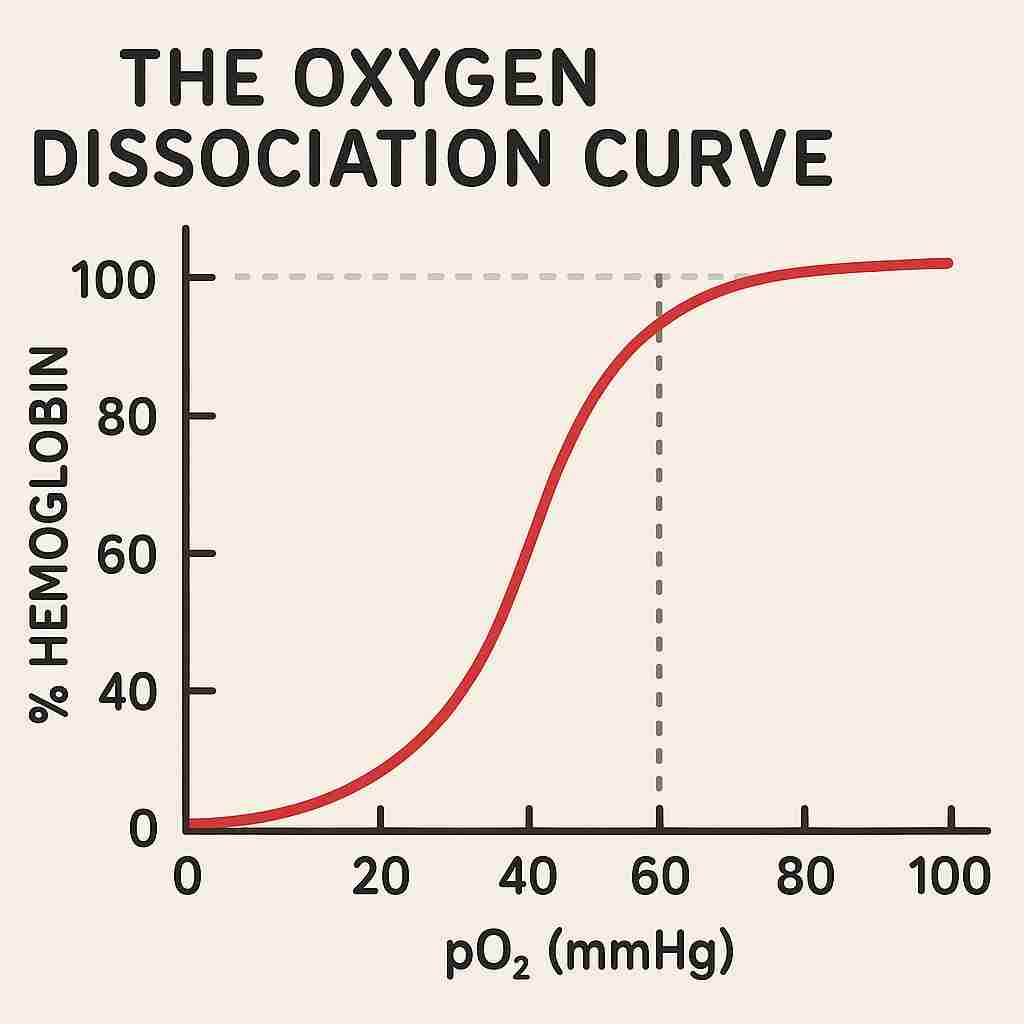
The oxygen dissociation curve is a graphical representation that illustrates the percentage saturation of hemoglobin with oxygen at varying partial pressures of oxygen (pO₂). The curve typically has a sigmoid or S-shaped appearance, reflecting the cooperative binding nature of hemoglobin.
At low pO₂ values, hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen is relatively low. However, as the pO₂ increases, the binding of the first oxygen molecule to hemoglobin enhances its affinity for subsequent oxygen molecules — a property known as cooperativity. As a result, the curve rises steeply in the middle range of pO₂.
At higher pO₂ levels, such as those present in the pulmonary alveoli, the curve plateaus, indicating that most of the hemoglobin molecules are nearly fully saturated with oxygen.
Significance of the Sigmoid Shape
The sigmoid shape of the oxygen dissociation curve is physiologically significant as it allows for efficient oxygen loading in the lungs and effective unloading in tissues. In the steep portion of the curve, a small decrease in pO₂ results in a significant release of oxygen from hemoglobin. This ensures that active tissues with slightly lower oxygen levels receive adequate oxygen supplies.
Conversely, in the plateau region, even substantial changes in pO₂ have little effect on the saturation level. This characteristic prevents excessive oxygen release in areas where it is not needed, ensuring a steady oxygen reserve within the blood.
Factors Affecting the Oxygen Dissociation Curve
Several physiological factors influence the position and shape of the oxygen dissociation curve. These include:
Effect of Carbon Dioxide
An increase in carbon dioxide concentration shifts the oxygen dissociation curve to the right. This shift signifies a decrease in hemoglobin’s oxygen-binding affinity, promoting oxygen release in tissues producing high amounts of carbon dioxide. This rightward shift due to elevated CO₂ is a classic example of the Bohr effect in action.
Effect of pH
A decrease in blood pH (acidosis) similarly shifts the oxygen dissociation curve to the right. The increased concentration of hydrogen ions stabilizes the T-form of hemoglobin, reducing its affinity for oxygen. Conversely, an increase in pH (alkalosis) shifts the curve to the left, enhancing oxygen binding.
Effect of Temperature
Elevated temperatures, typically occurring in metabolically active tissues, decrease hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen, shifting the curve to the right. This facilitates increased oxygen delivery to tissues where metabolic processes produce heat. Lower temperatures have the opposite effect, shifting the curve to the left.
Effect of 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG)
2,3-BPG is an organic phosphate compound produced in red blood cells during glycolysis. It binds to deoxygenated hemoglobin, reducing its affinity for oxygen and causing a rightward shift in the dissociation curve. This ensures enhanced oxygen release in tissues under physiological and hypoxic conditions.
Bohr Atomic Model
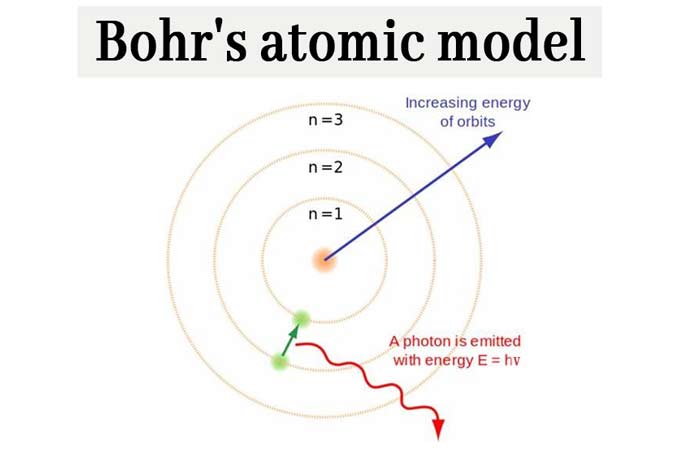
Though unrelated to the physiological Bohr effect, the Bohr atomic model remains an important concept in physics and chemistry. Proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913, this model introduced the idea that electrons orbit the atomic nucleus in fixed, quantized energy levels or shells. Unlike earlier atomic models, Bohr’s theory suggested that electrons do not continuously radiate energy while in these orbits, thereby explaining atomic stability.
When electrons move between these energy levels, they absorb or emit specific amounts of energy in the form of quanta or photons. This theory successfully explained the emission and absorption spectra of hydrogen and laid the groundwork for later developments in quantum mechanics. Although modern atomic theory has advanced beyond Bohr’s model, it remains a foundational concept in the study of atomic structure and behavior.
It is important to clarify that the Bohr atomic model and the Bohr effect in physiology are entirely different concepts, linked only by the scientist’s name.
Bohr Effect vs Haldane Effect
The Bohr effect and Haldane effect both describe gas exchange processes involving hemoglobin, but they differ in focus and conditions.
- The Bohr effect explains how increased CO₂ concentration or decreased pH lowers hemoglobin’s oxygen affinity, facilitating oxygen release to active tissues.
- The Haldane effect describes how oxygen binding to hemoglobin in the lungs reduces hemoglobin’s ability to carry CO₂. Oxygenated hemoglobin more readily releases CO₂, while deoxygenated hemoglobin binds CO₂ more effectively in tissues.
In short, the Bohr effect improves oxygen unloading in tissues, while the Haldane effect enhances CO₂ unloading in the lungs.
Bohr Effect: How CO₂ and pH Affect O₂ Binding
The mechanism underlying the Bohr effect involves a biochemical interplay between carbon dioxide, blood pH, and hemoglobin structure. In actively metabolizing tissues, increased CO₂ diffuses into red blood cells and reacts with water under the influence of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, forming carbonic acid (H₂CO₃). This weak acid quickly dissociates into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻).
The rise in hydrogen ion concentration lowers blood pH, causing hemoglobin to undergo conformational changes that reduce its affinity for oxygen. As a result, hemoglobin releases oxygen more readily, which then diffuses into tissues requiring it for cellular respiration.
At the same time, in the lungs, CO₂ diffuses out of the blood into alveolar air, reducing the hydrogen ion concentration and raising pH. This reversal restores hemoglobin’s higher oxygen affinity, allowing it to bind oxygen efficiently before transporting it back to tissues. This dynamic responsiveness of hemoglobin to changes in CO₂ and pH is critical for matching oxygen delivery with metabolic demand.
Physiological Importance of the Bohr Effect
The Bohr effect is vital for efficient gas exchange and tissue oxygenation. In actively metabolizing tissues, higher CO₂ production and lower pH conditions promote oxygen release where it is most needed. Conversely, in the oxygen-rich environment of the lungs, lower CO₂ levels and higher pH enhance oxygen binding. This adaptive mechanism ensures optimal delivery of oxygen during exercise, stress, or increased metabolic demand, contributing to the body’s ability to maintain homeostasis.
Enhanced Oxygen Delivery in Active Tissues
In metabolically active areas such as muscles during exercise, increased CO₂ and reduced pH enhance oxygen release, meeting heightened energy demands.
Efficient Oxygen Loading in Lungs
In the oxygen-rich and low-CO₂ environment of the lungs, the Bohr effect is reversed, improving oxygen uptake by hemoglobin for systemic distribution.
Support in Various Conditions
The Bohr effect is crucial during physical exertion, fever, high altitudes, and stress, ensuring tissues receive appropriate oxygen supplies as metabolic rates increase.
Contribution to Homeostasis
By modulating oxygen delivery based on tissue needs, the Bohr effect maintains homeostasis and optimizes cellular respiration across varying physiological states.
Clinical Relevance of the Bohr Effect
The Bohr effect holds considerable clinical significance, especially in conditions involving altered carbon dioxide levels, pH changes, and tissue oxygen demand. In scenarios such as vigorous physical exercise, hemorrhage, shock, or respiratory disorders, the ability of hemoglobin to efficiently unload oxygen becomes critically important.
Understanding the Bohr effect aids clinicians in managing patients with respiratory failure, metabolic acidosis, or those undergoing mechanical ventilation. It also provides insights into oxygen delivery mechanisms in high-altitude environments, anemia, and during certain surgeries.
Conclusion
The Bohr effect and the oxygen dissociation curve together play a vital role in regulating oxygen transport and delivery in the human body. By modulating hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen in response to carbon dioxide levels, pH, temperature, and other factors, these mechanisms ensure that oxygen is efficiently loaded in the lungs and unloaded in the tissues.
The interplay between carbon dioxide, pH, and hemoglobin’s oxygen affinity, as illustrated by the Bohr effect, highlights the dynamic nature of physiological systems in maintaining homeostasis. A thorough understanding of these processes is essential for students, physiologists, and healthcare professionals, as it forms the basis for interpreting respiratory and cardiovascular function in both health and disease.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the Bohr effect?
The Bohr effect is the decrease in hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen when carbon dioxide levels rise or blood pH drops, promoting oxygen release to active tissues.
What are the Bohr and Haldane effects?
The Bohr effect describes how CO₂ and low pH reduce hemoglobin’s oxygen affinity, aiding oxygen release. The Haldane effect explains how oxygen binding in the lungs helps release carbon dioxide from blood.
What is the Bohr effect in A-level Biology?
In A-level Biology, the Bohr effect refers to how increased CO₂ or lower pH in tissues causes hemoglobin to release more oxygen, shown by a rightward shift in the oxygen dissociation curve.