Biosafety Cabinet (BSC) is an enclosed, ventilated laboratory workspace known as a is intended to shield users, the surrounding environment, and work materials from potentially hazardous aerosols and splashes that may arise from handling potentially hazardous materials like chemicals or pathogens.
Enclosed and vented workstations known as biosafety cabinets are made to keep people, the environment, and the work being done safe from potentially dangerous biological agents. By sterilizing or filtering the air, they provide a controlled environment that stops the spread of infectious materials.
Table of Contents
Biosafety Cabinets
Classes of Biosafety Cabinets
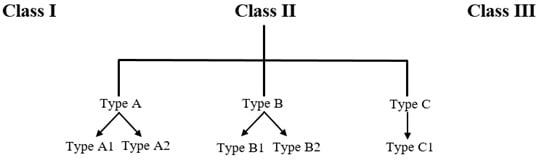
Based on how they are made and how much protection they provide, biosafety cabinets are divided into three classes: Class I, Class II, and Class III.
Class I Biosafety Cabinets
- Class I cabinets shield workers and the surroundings, but they do not shield the product, which is the substance being worked on.
- Airflow: The airflow is directed away from the operator and is not recirculated. After entering the cabinet, the air is filtered by a HEPA filter and then released.
- Use: Appropriate for tasks involving biological agents with low to moderate risk when product protection is not an issue.
- Applications: Aerosol-producing processes as well as general microbiological activity.
Class II Biosafety Cabinets
- Class II cabinets offer protection for products, workers, and the environment.
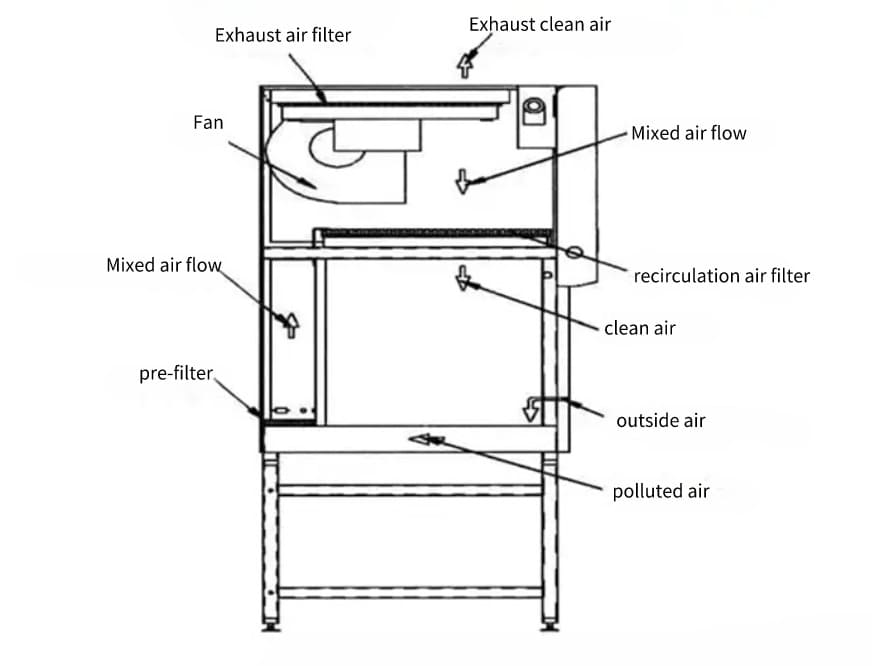
- Airflow: There is vertical laminar airflow within these cabinets. Before entering the work area, the inflow air is HEPA-filtered after being taken in through the front grille. Additionally, the exhaust air is HEPA-filtered.
- Subtypes: There are four types of Class II cabinets: A1, A2, B1, and B2.
- Type A1: ideal for working with low-risk materials because 70% of the air is cycled.
- Type A2: With higher air velocity than A1, this type is comparable.
- Type B1: Suitable for working with low to moderate risk materials, 70% of the air is expelled and ducted to the outside.
- Type B2: ideal for working with volatile chemicals and radionuclides, 100% of the air is vented and ducted outdoors.
Applications: Tissue culture, virology, pharmaceutical procedures, and research involving pathogens.
Class III Biosafety Cabinets
- Glove boxes, or Class III cabinets, offer the maximum level of protection for products, workers, and the environment.
- Airflow: Gloves are affixed, and procedures are carried out inside these fully enclosed, gas-tight devices. HEPA filters are used to draw air into the cabinet. To exhaust the air, either two HEPA filters are used in series, or one HEPA filter is used and then burned.
- Use: When working with biological agents that represent a serious risk to human health and are classified as high-risk (Biosafety Level 4).
- Applications: Managing dangerous or highly contagious materials; this includes working with diseases like smallpox and Ebola.
Types of Biosafety Cabinets
In addition to being divided into classes I, II, and III according to the level of protection they provide, BSCs can also be divided into groups according to particular functionalities and design elements.
Recirculating Type: Usually found in Class II Type A cabinets, these BSCs recirculate some of the air inside the cabinet following HEPA filtration.
Ducted Type: Found in Class II Type B and Class III cabinets, these BSCs are linked to the building’s exhaust system to provide a direct exhaust of air outside the facility.
Bench-Top Type: Conventional BSCs set up on lab benches.
Console Type: Unlike bench-top versions, these BSCs are floor-mounted devices that are frequently larger and offer greater workspace.
Selecting the Right Biosafety Cabinet
The following criteria influence the selection of a biosafety cabinet:
- The particular biological agent that is employed.
- The degree of safety needed for the product, the environment, and the workforce.
- The spending limit and the amount of space available.
- The particular methods and applications being used.
Applications of Biosafety
Biosafety is crucial in various settings, including
- Research and diagnostic labs that work with infectious agents are called laboratories.
- Healthcare Facilities ,Clinics and hospitals that treat patients with contagious illnesses.
- Facilities engaged in the research, development, and manufacture of vaccines, biologics, and other medicinal agents are classified as biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries.
- Facilities for plant and animal pathogen research and development.
- Monitoring infectious illness outbreaks and responding to them.
Summary
When it comes to safeguarding workers, the environment, and the integrity of work involving dangerous biological agents, biosafety cabinets are essential. By being aware of the many classes and kinds of cabinets, technicians and researchers can select the best solution for their particular requirements, guaranteeing a secure and regulated laboratory setting. Because they offer vital protection for workers, the environment, and the items being handled, biosafety cabinets are indispensable instruments for maintaining laboratory safety. They can be used in a variety of biological research and clinical laboratory settings and are divided into three primary classes (I, II, and III), each of which offers varying degrees of protection.
Frequent Asked Questions(FAQ)
Define Biosafety Cabinets?
Biosafety Cabinet (BSC) is an enclosed, ventilated laboratory workspace known as a is intended to shield users, the surrounding environment, and work materials from potentially hazardous aerosols and splashes that may arise from handling potentially hazardous materials like chemicals or pathogens.
What is the difference between Class 2 and Class 3 biosafety cabinet?
The second class, which is separated into subtypes based on differences in exhaust systems, offers safety for users, environments, and samples. Glove boxes, or Class III, are the last and are renowned for providing the highest level of security.
What are the 4 types of biosafety?
BSL-1, BSL-2, BSL-3, and BSL-4 are the four biosafety levels; BSL-4 is the highest (maximum) level of containment. Additional special guidelines and abbreviations apply to studies involving animals (ABSL), agriculture (BSL-Ag), and other subjects.
What is a Class III biological safety cabinet also called?
BSL-1, BSL-2, BSL-3, and BSL-4 are the four biosafety levels; BSL-4 is the highest (maximum) level of containment. Additional special guidelines and abbreviations apply to studies involving animals (ABSL), agriculture (BSL-Ag), and other subjects.
Related Article