Bioinformatics is a multidisciplinary field that combines biology, computer science, and information technology to analyze and interpret biological data .In order to analyze and understand biological data, the multidisciplinary area of bioinformatics combines computer science, biology, and information technology. For a variety of uses, it significantly depends on databases, applications, and software.
A new field known as bioinformatics was born out of the need to build computer tools for managing and analyzing the growing volume of biological data.
The study of the creation and use of computational tools for the analysis and interpretation of biological data is the focus of the quickly expanding discipline of bioinformatics in biology. Biological data is processed, stored, analyzed, and interpreted using databases, tools, and bioinformatics software.
Table of Contents
Bioinformatics Databases
GenBank
- Use: Nucleotide sequence databases from different organisms.
- Description: Offers all DNA sequences that are available to the public in annotated collections.
Protein Data Bank (PDB)
- Use: Large biological molecules’ 3D structural data repository.
- Description: Provides details on the physical configuration of nucleic acids and proteins.
UniProt
- Use: Extensive database of functional and sequencing data for proteins.
- Features functional information through the inclusion of protein sequences and annotations.
Ensembl
- Use: Vertebrate and other eukaryotic species’ genome databases.
- Description: Offers functional annotation and genomic assemblies for a variety of species.
NCBI Gene
- Use: Gene-specific data centralized store.
- Encompasses gene sequences, gene products, and their respective roles.
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)
- Use: A database to comprehend the higher-level capabilities and uses of biological systems.
- Information about medications, chemicals, diseases, biological pathways, and genomes is provided.
dbSNP
- Use: Multiple small-scale variations and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) database.
- Information on genetic variants in various creatures is provided.
Bioinformatics Software and Tools
BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)
- Use: Verifies protein or nucleotide sequences against sequence databases.
- Finds commonalities and aids in comprehending evolutionary and functional links.
Clustal Omega
- Utilize: Tool for multiple sequence alignment.
- Description: Infers evolutionary links by aligning three or more biological sequences.
MEGA (Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis)
- Use: A tool for molecular evolution statistical analysis.
- Features tools for building phylogenetic trees, aligning sequences, and evaluating evolutionary hypotheses.
Bioconductor
- Use: Bioinformatics open-source software, particularly for genetic data analysis.
- Tools for interpreting and analyzing high-throughput genomic data are included.
Cytoscape
- Use: Complex network visualization software.
- Utilized to combine high-throughput expression data with biomolecular interaction networks.
Galaxy
- Use: Web-based platform for biomedical research using large amounts of data.
- Description: Makes computational research transparent, repeatable, and approachable.
PyMOL
- Utilize: A technique for seeing molecules.
- Used to visualize protein structures and other macromolecules in three dimensions.
GROMACS
- Use: Software for simulating molecular dynamics.
- Description: For systems with hundreds to millions of particles, this tool is used to simulate the Newtonian equations of motion.
T-Coffee
- Utilize: Program for multiple sequence alignment.
- Offers a structure for aligning DNA, RNA, or protein sequences.
Bowtie
- Use: A short-read sequence aligner that is quick and memory-efficient.
- Used to align sequencing reads to lengthy reference sequences, according to the description.
Specific Uses
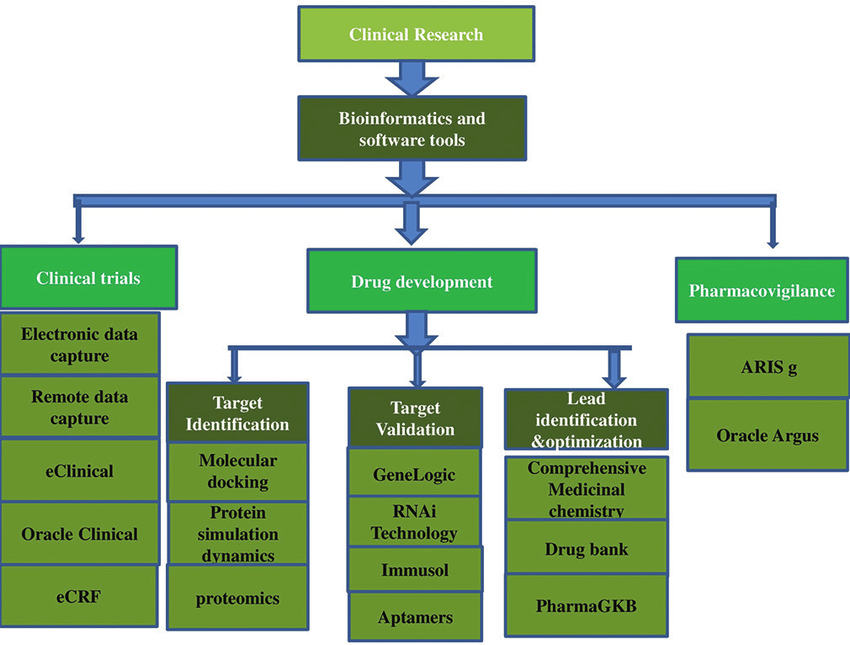
Genomic Research: Sequence alignment, variation identification, and genomic data analysis depend heavily on programs like BLAST, Bowtie, and GATK.
Proteomics: For protein sequence analysis and 3D structure visualization, UniProt and PyMOL are crucial tools.
Structural Biology: Data and resources for studying the structures of biomolecules can be found in PDB and PyMOL.
- Systems biology: KEGG and Cytoscape facilitate the comprehension of biological system and pathway relationships.
- Transcriptomics: RNA sequencing data interpretation and gene expression analysis are performed using programs such as Clustal Omega and Bioconductor.
- Data Integration and Visualization: To help with data interpretation, Galaxy and Cytoscape offer visualization tools and make it easier to combine various biological data types.
Importance of Biological Databases
- Large volumes of biological data can be structured and arranged thanks to biological databases.
- A valuable tool for researchers to use in their work is a biological database.
- Utilizing biological datasets, new bioinformatics techniques and tools can be created to promote additional study.
- Additionally, biological databases make it easier for researchers to collaborate and share resources and data.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
Define Bioinformatics Databases ?
Bioinformatics Databases is a multidisciplinary field that combines biology, computer science, and information technology to analyze and interpret biological data .
What database is used in bioinformatics?
Swiss Prot from the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, PIR from the Protein Information Resource, and GenBank from the National Center for Biotechnology Information are a few well-known databases.
What are the 3 types of databases in bioinformatics?
Biological databases can be further classified as primary, secondary, and composite databases.
What are the applications of bioinformatics?
Gene therapy, customized medicine, preventative medicine, and drug discovery are some of its uses.
Related Article