Streptococcus pyogenes Gram-positive is a major human pathogen that causes a range of infections from pharyngitis (strep throat) to more serious conditions like rheumatic fever and necrotizing fasciitis. Several biochemical assays are used in clinical laboratories to reliably identify S. pyogenes.
Group A Streptococcus (GAS), or Streptococcus pyogenes, is an important pathogen that causes a variety of human diseases, ranging from minor ailments like pharyngitis (strep throat) to more serious problems like necrotizing fasciitis and rheumatic fever. In clinical laboratories, S. pyogenes is accurately identified by a battery of biochemical assays that differentiate it from other streptococci and related bacteria. The main biochemical techniques used to detect S. pyogenes are explained in detail below.
Table of Contents
Streptococcus pyogenes
Hemolysis on Blood Agar
Beta-hemolysis is seen in Streptococcus pyogenes pyogenes on blood agar plates. This indicates that because of the total lysis of red blood cells, it creates transparent, colorless zones surrounding its colonies. The synthesis of two hemolysins, streptolysin O and streptolysin S, is what causes this particular hemolysis. While streptolysin S is oxygen-stable and causes hemolysis when oxygen is present, streptolysin O is oxygen-sensitive and its activity is increased in anaerobic environments.
Catalase Test
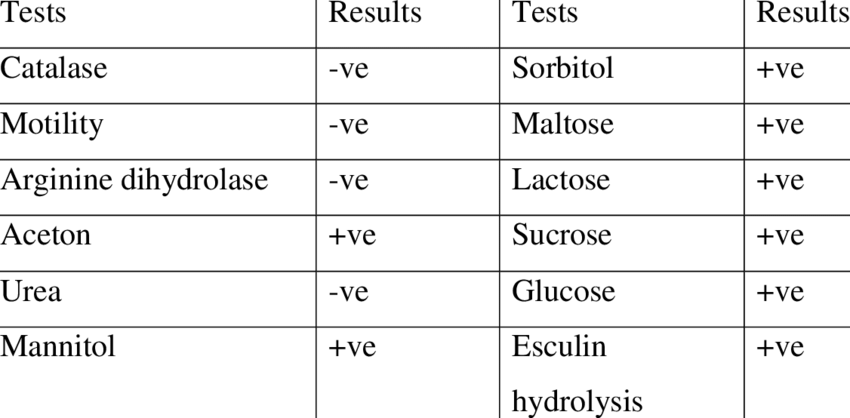
The catalase test involves applying hydrogen peroxide to a bacterial culture and looking for bubbles to distinguish catalase-producing bacteria from non-producers. Because S. pyogenes lacks the enzyme catalase, which converts hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, it is catalase-negative. It can be distinguished from catalase-positive Staphylococcus species thanks to this trait.
Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
Bacitracin is susceptible to S. pyogenes. A bacitracin disk is put on a blood agar plate that has been infected with the bacteria in this test. A zone of inhibition surrounding the bacitracin disk after incubation denotes susceptibility. When separating S. pyogenes from other beta-hemolytic streptococci—which are typically resistant to bacitracin—this test is especially helpful.
PYR Test (Pyrrolidonyl Arylamidase Test)
Pyrrolidonyl arylamidase (PYR) is the enzyme produced by S. pyogenes. When a certain reagent is introduced, this enzyme hydrolyzes the substrate L-pyrrolidonyl-β-naphthylamide, changing its hue. A positive result verifies the existence of PYR and is denoted by a red or pink hue. This test is an efficient and accurate way to distinguish S. pyogenes from other streptococci.
Hippurate Hydrolysis Test
The hippurate hydrolysis test aids in distinguishing between streptococci belonging to Groups A and B. Because S. pyogenes is hippurate-negative, it cannot hydrolyze sodium hippurate to produce glycine and benzoic acid. Streptococcus agalactiae, or Group B Streptococcus, on the other hand, is hippurate-positive.
CAMP Test
The CAMP test measures the amount of the CAMP factor produced, which increases Staphylococcus aureus beta-lysin’s hemolytic activity on blood agar. Because S. pyogenes lacks CAMP, it does not exhibit increased hemolysis when S. aureus is present. It can be distinguished from CAMP-positive S. agalactiae with the aid of this test.
Group A Streptococcal Antigen Test
Bacterial cell walls contain Group A carbohydrate antigens that can be found using rapid antigen detection tests (RADTs). Using throat swabs, these assays offer a rapid and accurate way to identify S. pyogenes. If the test is positive, Group A streptococcal antigens are present.
Sugar Fermentation Tests
Glucose, lactose, and sucrose are among the carbohydrates that S. pyogenes can ferment, yielding acid without releasing gas. By cultivating the bacteria in media containing the particular sugars and a pH indicator, these fermentation capabilities are evaluated. The medium changes color due to the generation of acid, signifying fermentation.
Esculin Hydrolysis Test
S. pyogenes is distinguished from Group D streptococci and Enterococci by the esculin hydrolysis test. Because S. pyogenes lacks esculin, it is unable to hydrolyze esculin into esculetin and glucose. A negative result contrasts with the positive blackening seen with esculin-positive bacteria in that it indicates no change in medium color.
Conclusion
In clinical circumstances, S. pyogenes can be precisely identified by combining these biochemical tests. A trustworthy framework for S. pyogenes identification is provided by its distinctive beta-hemolysis, catalase negativity, bacitracin susceptibility, positive PYR test, hippurate negativity, CAMP negativity, fast antigen detection, particular sugar fermentation profiles, and esculin negativity. For this pathogen to generate infections that need to be clinically managed and treated, accurate identification is essential.
Frequently Asked Question(FAQ)
Define Streptococcus pyogenes ?
Streptococcus pyogenes Gram-positive is a major human pathogen that causes a range of infections from pharyngitis (strep throat) to more serious conditions like rheumatic fever and necrotizing fasciitis.
What biochemical test is used to identify Streptococcus pyogenes?
Since other β-hemolytic strains of streptococci that might possess the group A antigen are resistant to bacitracin, the bacitracin test is used in conjunction with the Lancefield antigen A test for greater specificity in the identification of S. pyogenes.
What is the laboratory test for Streptococcus pyogenes?
As mentioned below, cultures should be examined for PYR activity and bacitracin susceptibility in order to make an educated guess about the identity of S. pyogenes. A positive Lancefield group A antigen test should be part of a definite diagnosis. It is possible to confirm negative results following a 48-hour total culture time.
What is the quick test for Streptococcus pyogenes?
The components in the Strep antigens are a microorganism that makes your body fight the virus by boosting immunity. Results from a fast strep test can be obtained in 10–20 minutes.
Related Article