Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a Gram-negative, oxidase-positive, catalase-positive diplococcus that ferments glucose but not maltose, lactose, or sucrose. It produces a vigorous bubble reaction in the superoxol test and is negative for nitrate reduction, DNA hydrolysis, and butyrate esterase production. These biochemical characteristics help in differentiating it from other Neisseria species and related bacteria.
A strong reactivity in the superoxol test, positive oxidase and catalase tests, and the capacity to ferment glucose (but not maltose, lactose, or sucrose) are characteristics of this. It doesn’t hydrolyze DNA, convert nitrate to nitrite, or generate butyrate esterase. Treatment for this virus can be difficult due to its capacity to elude the human immune system and acquire resistance to several drugs. These biochemical characteristics help in differentiating Neisseria gonorrhoeae from other Neisseria species and related bacteria.
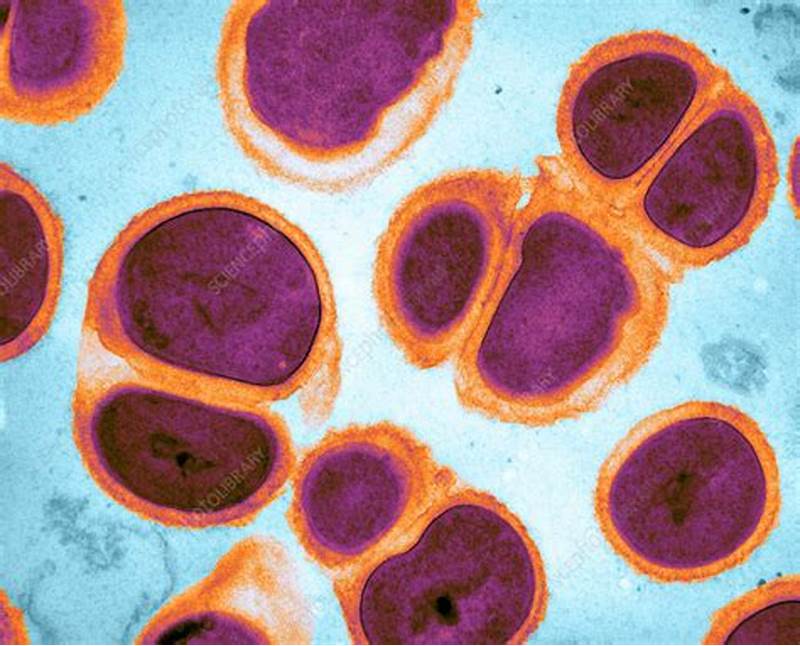
Table of Contents
Definition of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
The aerobic, facultatively intracellular, Gram-negative bacterium takes the form of kidney-shaped diplococci, or pairs of cocci. It is responsible for gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted illness (STI) that affects the rectum, throat, eyes, and mucous membranes of the reproductive system. A strong reactivity in the superoxol test, positive oxidase and catalase tests, and the capacity to ferment glucose (but not maltose, lactose, or sucrose) are characteristics of this. It doesn’t hydrolyze DNA, convert nitrate to nitrite, or generate butyrate esterase. Treatment for this virus can be difficult due to its capacity to elude the human immune system and acquire resistance to several drugs.
Biochemical Test of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Gram Staining
The outcome is Gram-negative. It is a type of coccus that stains pink. They are usually seen in pairs, or diplococci, with flattened sides, resembling kidney beans.
Oxidase Test
The outcome is Positive. Cytochrome oxidase, produced by this, combines with the oxidase reagent to produce a dark purple color.
Catalase Test
The outcome is outcome Positive. The bacterium is the producer of the catalase enzyme, which splits hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen and causes bubbles
Carbohydrate Utilization Test
The fermentation of glucose by this yield’s acid, which is indicated by a pH indicator turning yellow. The fermentation process produces a positive result.
Superoxol Examination
The outcome is Positive. Because it has a high catalase activity, 30% hydrogen peroxide causes a quick and intense bubble reaction.
Nitrate Reduction Test
The outcome is Negative. This does not produce butyrate esterase, resulting in no color change when a butyrate disk is used.
Morphology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- When viewed under a microscope, it resembles a gram-negative coccus that flattens the sides of its companions and is found in pairs (diplococci).
- The diameter is between 0.6 and 1 μm.
- The diplococci are shaped like kidney or coffee beans.
- It is a bacterium that does not generate spores and moves by twitching.
- Pinholes are seen on the surface of gonococci.
- Pili increases the cocci’s ability to adhere to mucosal surfaces and, by preventing phagocytosis, increases pathogenicity.
- Piliated gonococci agglutinate human red blood cells, but not those of other mammals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Neisseria gonorrhoeae?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a Gram-negative, diplococcal bacterium responsible for causing gonorrhea, a common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
How is Neisseria gonorrhoeae transmitted?
It is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. It can also be transmitted from mother to baby during childbirth.
What are the key biochemical characteristics of Neisseria gonorrhoeae?
Key biochemical characteristics include being oxidase-positive, catalase-positive, and the ability to ferment glucose but not maltose, lactose, or sucrose.
Related Articles

