The Bile Esculin Test is an important diagnostic test in clinical microbiology for identifying and distinguishing some gram-positive cocci, particularly Enterococcus species and some members of the Streptococcus bovis group. By making use of these bacteria’s particular capacity to hydrolyze esculin in the presence of bile salts, the test provides a simple and reliable method of identifying them from other streptococci. This assay is especially valued for its simplicity, effectiveness, and function in facilitating the diagnosis of infections caused by these bacteria, making it an indispensable tool in the microbiologist’s toolbox.
Table of Contents
What is the Bile Esculin Test?
The Bile Esculin Test is a microbiological technique that detects bacteria capable of hydrolyzing esculin in the presence of bile salts. It aids in distinguishing some gram-positive cocci, such as Enterococcus species and Streptococcus bovis group members, from other organisms. The breakdown of esculin causes a dark color change in the medium, indicating positive results.
Principle – Bile Esculin Test
- The test is based on the hydrolysis of esculin in the presence of bile salts.
- Esculin is a glucoside molecule made up of glucose and hydroxycoumarin connected by an ester bond.
- Organisms are initially chosen for their capacity to grow in a medium containing 4% bile salts.
- Then they are chosen based on their ability to hydrolyze esculin.
- Esculin hydrolysis yields both glucose and esculetin.
- Esculetin interacts with iron ions (from ferric citrate) in the medium, producing a dark brown or black color.
- Alternatively, esculin is a fluorescent molecule whose hydrolysis can be detected by a loss of fluorescence.
Procedure – Bile Esculin Test
1. Preparation
Acquire slants or agar plates for bile esculin. Bile salts, esculin, ferric citrate, and other nutrients are present in them.
2. Inoculation
For plates: Apply the test organism to the bile esculin agar surface.
For slants: Use a loop carrying the test organism to streak the slant and stab the butt.
3. Incubation
For 24 to 48 hours, incubate the plates or slants at 35 to 37°C.
4. Observation
Look for any color changes in the medium after incubation.
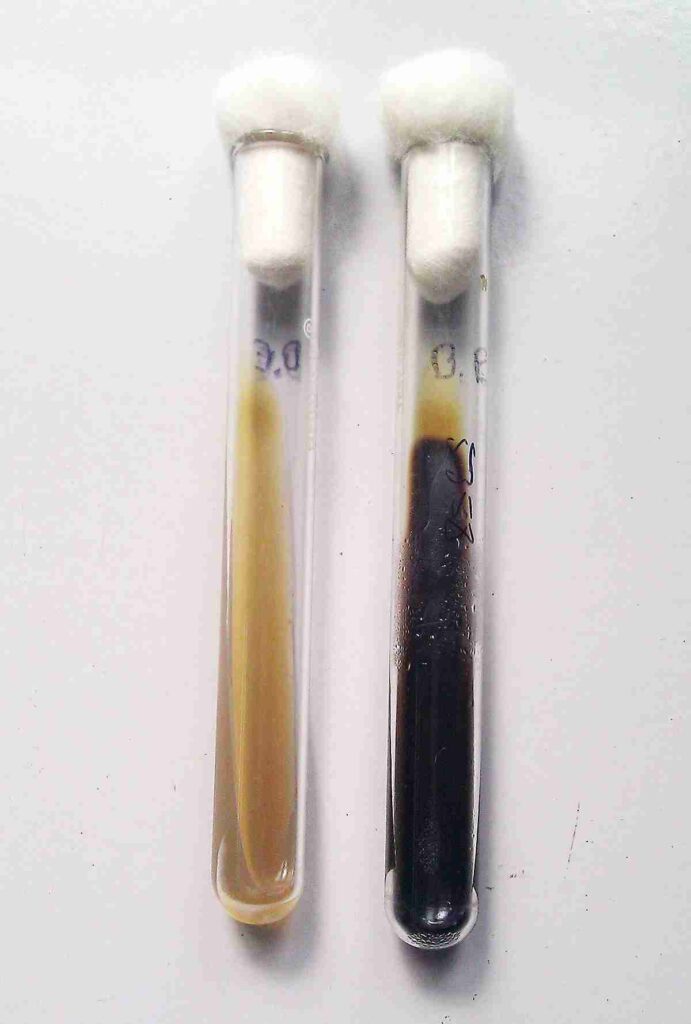
Results
- Positive Result: If the medium turns dark brown or black, it indicates that the organism can hydrolyze esculin in the presence of bile. This is a positive result.
- Negative Result: If the medium remains its original color (typically a light yellow or unchanged), it indicates a negative result for esculin hydrolysis.
Uses
- Identification of Enterococcus species:
These bacteria can grow in bile and hydrolyze esculin. - Differentiation of Group D Streptococci:
Enterococci and some Streptococcus bovis strains can be distinguished from other streptococci. - Diagnostic Aid:
Used in clinical microbiology to identify harmful microorganisms in clinical samples.
Limitations
- False positives
Certain non-Enterococcus and non-Group D Streptococcus bacteria may also hydrolyze esculin, resulting in false positives. - Environmental conditions
Some Enterococci may not hydrolyze esculin in certain environments or may require longer incubation durations. - Non-Specific Growth
While bile salts block many gram-positive organisms, they are not selective, and non-target species may continue to grow and hydrolyze esculin. - Quality of medium
The test’s reliability is determined by the quality of the bile esculin medium, which includes the right concentrations of bile salts and ferric citrate.
To summarize, the Bile Esculin Test is an important and dependable method for identifying Enterococcus species and some Streptococcus bovis group members from other gram-positive bacteria. Its premise of esculin hydrolysis in the presence of bile yields a clear and conclusive result, making it an important tool in clinical microbiology for reliable bacterial detection. Despite its limitations, such as the possibility of false positives and the necessity for a high-quality medium, the test remains an important tool in the detection of infections caused by these organisms. The Bile Esculin Test is essential for effective bacterial infection management and therapy because it allows for rapid and accurate identification.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the purpose of the Bile Esculin test?
The test is designed to discover microorganisms that can hydrolyze esculin in the presence of bile salts.
How Does the Bile Esculin Test Work?
Bacteria that hydrolyze esculin create esculetin, which interacts with ferric citrate in the medium, changing the hue to dark brown or black.
What is the importance of the Bile Esculin Test in clinical microbiology?
It is an effective technique for diagnosing infections caused by Enterococcus species and associated bacteria, allowing for more informed treatment options.
Related Articles