Batch ,Fed Batch , Continuous Culture belongs to microbial culture method.
Table of Contents
Batch Culture Definition
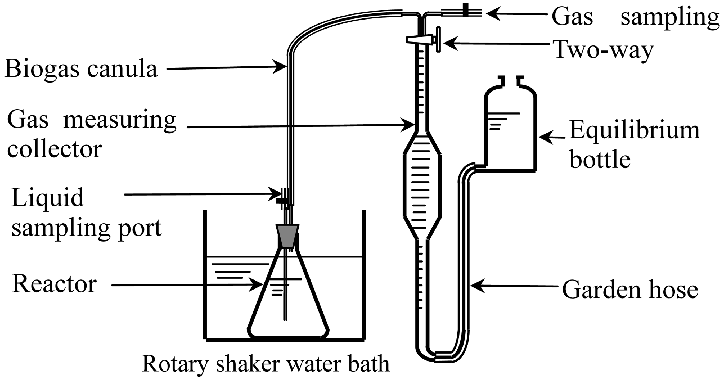
One kind of microbial culture technique in which microorganisms are cultivated in a closed system with a set volume of nutrient solution. With this approach, all nutrients are provided at the start of the cultivation process, and no more are added while the plant is growing. The culture is let to go through different stages of bacterial growth until waste products build up to an inhibiting level or the nutrients run out.
Key characterstics
- Closed System: After the initial setup, the culture is kept inside a vessel that doesn’t interchange matter with its surroundings.
- Nutrient Supply: During the culture period, all necessary nutrients are supplied at the beginning and are not added again.
Fed Batch culture
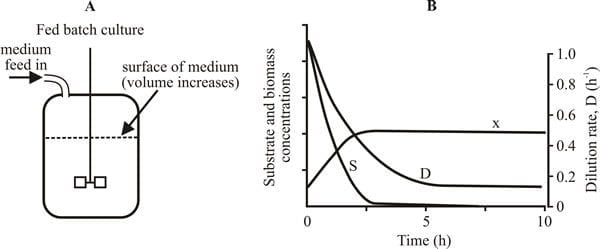
It is a bioprocessing method wherein cells or microorganisms are cultivated while having fresh nutrients delivered to the culture on a regular or continuous basis, all the while retaining the culture medium. By supplying the required nutrients gradually, avoiding nutrient depletion, and reducing the buildup of hazardous byproducts that could impede growth, this strategy enables prolonged growth phases, usually the logarithmic (log) phase.
Key characterstics
- The culture process involves the intermittent or continual addition of nutrients.
- The precise needs of the microbes or cells can be used to precisely manage the timing and amount of nutrition supply.
- During the feeding phase, the culture is maintained in a closed system with no removal of culture medium.
- The culture’s volume may progressively grow over time; only nutrients are introduced.
Continuous Culture
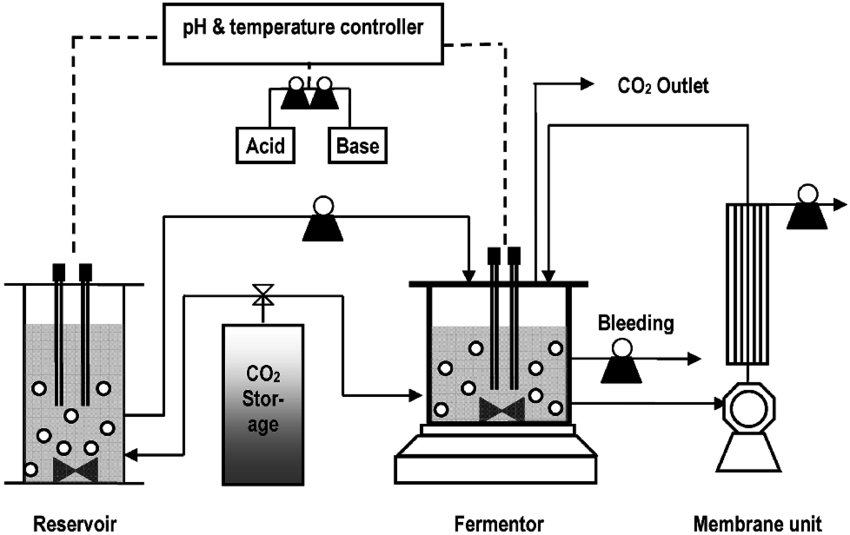
A comparable volume of spent medium comprising cells, c, and waste is concurrently withdrawn from the culture vessel while fresh nutrient media is continuously added. This bioprocessing approach is known as continuous culture. This technique keeps steady-state conditions and a constant culture volume, enabling the long-term, uninterrupted development of microorganisms or cells.
key characterstics
- The culture is constantly receiving fresh nutrients, which ensures a steady supply of the vital elements needed for growth.
- The fresh medium is continuously introduced at the same rate as the spent medium, cells, and byproducts are withdrawn. This aids in preserving a steady amount of culture.
Batch vs Fed-Batch vs Continuous Culture
| S.N | Batch Culture | Fed batch culture | continuous culture |
| 1. | All of the medium’s ingredients are added to the reactor at the beginning of the cultivation process in this fermentation. | An adaptation of this fermentation where nutrients are added routinely . | It is a procedure in which the bioreactor is continuously supplied with nutrients while also removing the culture broth, which contains cells and metabolites. |
| 2. | There are no additional fertilizer additives made after the initial stages of production. | During the cultivation phase, the nutrients are first provided and then progressively added. | Throughout the cultivation process, nutrients are continuously added, and the finished product is continuously removed. |
| 3. | A closed system is used to carry out the fermentation process. | A system that is partially closed is used for fermentation. | An open system is used for the fermentation process. |
| 4. | It is a discontinuous process | It is a semi-continuous process | It is a continuous process. |
| 5. | Microorganisms experience four stages. Phase lag Phase of logs stationary stage Phase of death | Microorganisms experience four stages. Phase lag Phase of logs stationary stage Phase of death | Microorganisms are maintained at lag and log phases throughout the process |
| 6. | The procedure comes to an end when the products are formed. | When the products are formed, the whole process is halted | The products are continuously taken out of the fermentor as the process proceeds. |
| 7. | The environment within changes throughout time. | The environment within stays unchanged. | The internal environment remains constant. |
| 8. | Once the fermentation process starts, the arrangement is not changed. | As soon as the fermentation process starts, the outer environment changes. | The outer atmosphere changes as soon as the fermentation process starts. |
| 9. | The volume of nutrients remains the same. | The volume of nutrients increases. | The volume of nutrients remains the same. |
| 10. | Less control over the intended product and microbial proliferation exists during the procedure. | More control over the intended product and microbial growth exists during the procedure. | More control over the intended product and microbial growth exists during the procedure. |
| 11. | There is no chance of contamination and mutation. | There is a chance of contamination and mutation. | There is a chance of contamination and mutation |
| 12. | The turnover rate is low due to the restricted amount of nutrients and other circumstances inside. | As long as the ideal nutritional levels are preserved, the turnover rate is moderate. | The turnover rate is high because the ideal nutrition levels and other conditions are being maintained. |
| 13. | Operating this setup is easy. | This system is intricate and challenging to set up and manage. | Setting up this is challenging and complex to execute. |
| 14. | They are performed in large fermentors. | This are performed in small fermentors. | They are performed in small fermenters. |
| 15. | Product yield is low. | Product yield is high. | Product yield is high |
| 16. | It is mostly employed in the synthesis of byproducts like antibiotics. | It is primarily employed in the synthesis of recombinant proteins and alcohol. | It is mostly employed in the synthesis of primary metabolites like organic acids and amino acids. |
| 17. | Labor demand is less | Labor demand is high. | Labor demand is high. |
| 18. | Control methods are easy and quick | Control methods are complex and time-consuming | Control methods are complex and time-consuming |
| 19. | It required less investment. | It required high investment | It required high investment. |
| 20. | The product is harvested by a downstream process. | A process that happens downstream harvests the product. | Processing downstream is intricate. |
Frequently Asked Question(FAQ)
Define batch culture?
One kind of microbial culture technique is batch culture, in which microorganisms are cultivated in a closed system with a set volume of nutrient solution.
What is the difference between batch fed-batch and continuous culture?
Additional nutrients are not added until the very end of the this technique. Unlike continuous when nutrients are provided and products are continuously removed, fed-batch receive nutrient additions over a longer period of time.
What is the main difference between batch process and continuous process?
This processing offers superior quality control and traceability because all of the ingredients are combined at once. The continuous movement of ingredients through the system during processing, however, increases the danger of contamination.
What are the different types of batch culture?
It comes in several forms, including shaken, spinning, gently rotating, and stirred cultures.
Related Article