Bacitracin Susceptibility Test is a scientific method that determines bacteria’s susceptibility to bacitracin, an antibiotic generated by Bacillus subtilis. Bacitracin is most efficient against gram-positive bacteria and is often used to treat infections caused by Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species.
Table of Contents
Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
The Bacitracin Susceptibility Test is a laboratory method used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to bacitracin, an antibiotic primarily effective against gram-positive bacteria. This test is particularly useful in identifying bacteria such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species, which are commonly susceptible to bacitracin.
Principle of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
The Bacitracin Susceptibility Test works by assessing bacteria susceptibility to bacitracin, an antibiotic that is often used to treat gram-positive bacterial infections. Bacitracin is diffused from a standardized disc onto an agar plate that has been infected with the test organism. The principle works as follows:
Preparation of Agar Plate
A culture medium, usually Mueller-Hinton agar, is prepared and inoculated with the test organism using a sterile swab to establish a homogenous bacterial lawn.
Bacitracin Disc Placement
A paper disc or disk impregnated with a known concentration of bacitracin is placed onto the surface of the agar plate, ensuring good contact with the agar.
Incubation
The agar plate is incubated at the appropriate temperature (usually 35-37°C) for a specific duration, typically 18-24 hours.
Evaluation of Zone of Inhibition
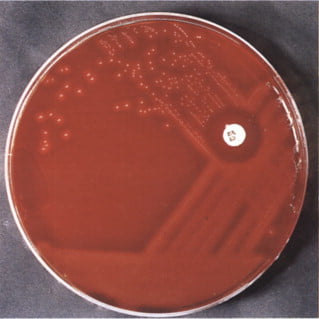
After incubation, the agar plate is examined for the presence of a zone of inhibition around the bacitracin disc. The zone of inhibition is an area where bacterial growth is inhibited due to the presence of bacitracin.
Interpretation of Results
The diameter of the zone of inhibition is measured with a ruler or caliper. The size of the zone correlates with the bacteria’s susceptibility to bacitracin. Larger zones indicate increased vulnerability, whereas smaller or nonexistent zones indicate resistance.
Reporting
Results are reported as susceptible, intermediate, or resistant based on established interpretive criteria provided by organizations such as the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) or the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST).
Procedure of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
Specimen Collection and Preparation
A pure culture of the organism that will be evaluated is obtained. Typically, a beta-hemolytic colony from a blood agar plate is utilized.
Inoculation
Use a sterile swab or loop to inoculate a Mueller-Hinton or blood agar plate with the test organism. The inoculum should be evenly distributed to promote a uniform lawn of bacterial growth.
Placement of Bacitracin Disk
A commercially manufactured bacitracin disk (often containing 0.04 units of bacitracin) is placed on top of the inoculated agar.
Incubation
The plate is kept at 35-37°C for 18-24 hours.
Observation
After incubation, inspect the plate for zones of inhibition around the bacitracin disk.
Result for Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
Susceptible
A clear zone of inhibition (usually 10 mm or more) surrounding the bacitracin disk suggests susceptibility. This is typical of Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococcus).
Resistant
Resistance is shown by a small or absent zone of inhibition around the bacitracin disk. Other beta-hemolytic streptococci, including Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Streptococcus), are often resistant.
Uses of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
Differentiation of Beta-Hemolytic Streptococci
The bacitracin susceptibility test is primarily used to identify Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A) from other beta-hemolytic streptococci.
Diagnostic Aid
It aids in the clinical diagnosis of Group A Streptococcus infections, including streptococcal pharyngitis, impetigo, and cellulitis.
Routine Laboratory Testing
It is a standard procedure in clinical microbiology laboratories to identify beta-hemolytic streptococci.
Screening for Carriers
In epidemiological research, the test can be used to identify carriers of Group A Streptococcus in a community.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is Bacitracin Susceptibility Test ?
The Bacitracin Susceptibility Test is a microbiological test that determines whether bacteria are susceptible or resistant to the antibiotic bacitracin. It is notably beneficial in distinguishing between specific types of Gram-positive cocci, particularly beta-hemolytic streptococci. The test works on the assumption that bacitracin can impede the development of sensitive bacteria by interfering with cell wall formation.
What are the Uses of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test?
The uses of Bacitracin Susceptibility test are:
Differentiation of Beta-Hemolytic Streptococci
Diagnostic Aid
Routine Laboratory Testing
Screening for Carriers
Related Article