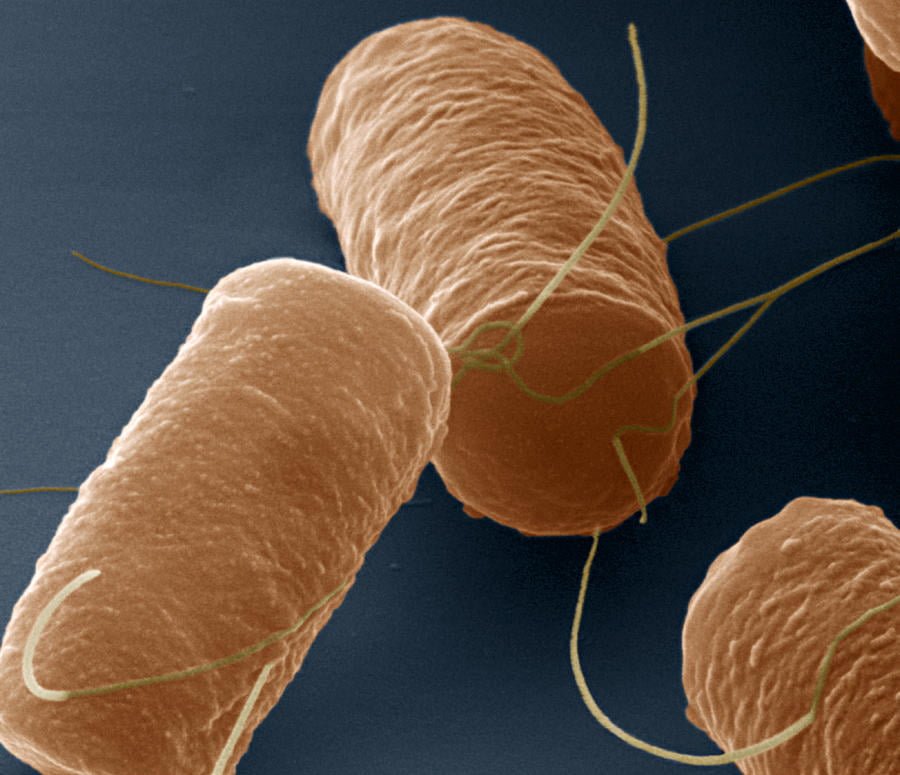
Bacillus cereus the rod-shaped, gram-positive bacterium is present in soil, plants, and food, among other environmental sources. It is well recognized to cause foodborne diseases, especially when toxins are produced. Based on the toxins generated and the ensuing symptoms, Bacillus cereus food poisoning is commonly divided into two categories: emetic (vomiting) and diarrheal .Spore-forming bacteria called Bacillus cereus are frequently found in soil, plants, and a wide range of foods. Because of its ability to withstand extreme circumstances, including high temperatures, it is frequently found as a contamination in food products.
Table of Contents
Bacillus cereus
Emetic Syndrome
- The emetic form of food poisoning is brought on by the heat-stable toxin cereulide.
- Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and sometimes cramping in the abdomen. Usually, symptoms start to show up one to five hours after eating tainted food.
- Duration: Within 24 hours, symptoms often go away.
- Common Foods are Carbohydrates like potatoes, pasta, and rice. One common reason is rice, either boiled or fried, that has been incorrectly preserved.
Diarrheal Syndrome
- Heat-labile enterotoxins, such as hemolysin BL (HBL), non-hemolytic enterotoxin (Nhe), and cytotoxin K, are the culprits behind the diarrheal type.
- Symptoms: cramping in the abdomen, diarrhea, and occasionally nausea. Usually, 6 to 15 hours after eating tainted food, symptoms appear.
- The duration of symptoms is typically between 24 and 48 hours.
- Common Foods: A wide range of foods, such as fish, vegetables, dairy products, and meats.
Pathogenesis
- Cereulide, an emesis toxin, is pre-formed in food and hence exists at the time of consumption. It is difficult to destroy with standard cooking techniques because of its great resistance to heat and acid.
- Diarrheal Toxins When Bacillus cereus spores or vegetative cells are consumed, the small intestine produces these toxins. In the gut, the bacteria proliferate, germinate, and create enterotoxins.
Prevention
- Handling Food Properly: Make sure food is cooked all the way through and kept at the right temperature. Cold foods should be stored below 4°C (40°F) and hot foods above 60°C (140°F).
- Hygiene: Maintain proper kitchen hygiene by routinely washing your hands, utensils, and surfaces.
- Quick Cooling: To stop the germination of spores and the creation of toxins, cool cooked food fast. Store leftovers in the refrigerator as soon as possible.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis: Based on a history of recent food consumption and the symptoms. Toxins produced by Bacillus cereus can be identified in a lab setting using food or stool samples.
Treatment: Mostly supportive, with an emphasis on symptom alleviation and fluids. The majority of instances resolve on their own and don’t require special medical attention. In severe circumstances, medical care can be necessary.
Conclusion
Food poisoning caused by Bacillus cereus is a common but avoidable gastrointestinal ailment. The risk of infection can be considerably decreased by comprehending the different sorts of toxins involved and putting appropriate food safety procedures into effect. The illness known as “Bacillus cereus food poisoning” is brought on by eating food tainted with the bacteria or its toxins. Depending on the kind of toxin involved, there are two different ways that this kind of food poisoning presents itself: the emetic (vomiting) form and the diarrheal form.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
Define Bacillus cereus ?
Bacillus cereus the rod-shaped, gram-positive bacterium is present in soil, plants, and food, among other environmental sources. It is well recognized to cause foodborne diseases, especially when toxins are produced.
What is Bacillus cereus poisoning?
The foodborne pathogen Bacillus cereus can create toxins that can lead to two different gastrointestinal illnesses: the diarrhoeal syndrome and the emetic (vomiting) syndrome.
Is Bacillus cereus killed by heat?
If food reaches a temperature of ≥ 145ºF (63ºC), the vegetative cells and spores will be destroyed by pressure-steaming, roasting, frying, and grilling.
What food has Bacillus cereus?
One type of bacteria commonly found in starchy foods is Bacillus cereus. Rice, powdered dairy products, and dry potato flakes are examples of starchy foods.
Related Article