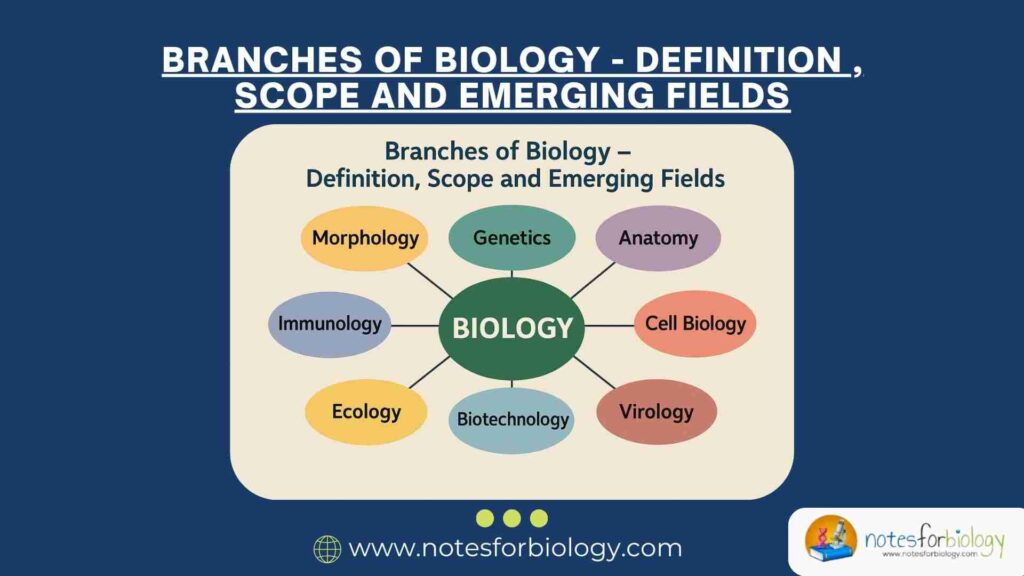
Branches of Biology – Definition , Scope and Emerging Fields
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms, encompassing their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and classification. It is a vast field that integrates various sub-disciplines focusing on different aspects of life. Over time, as biological knowledge expanded, it became essential to classify the study of life into different branches. Each branch […]
Branches of Biology – Definition , Scope and Emerging Fields Read More »