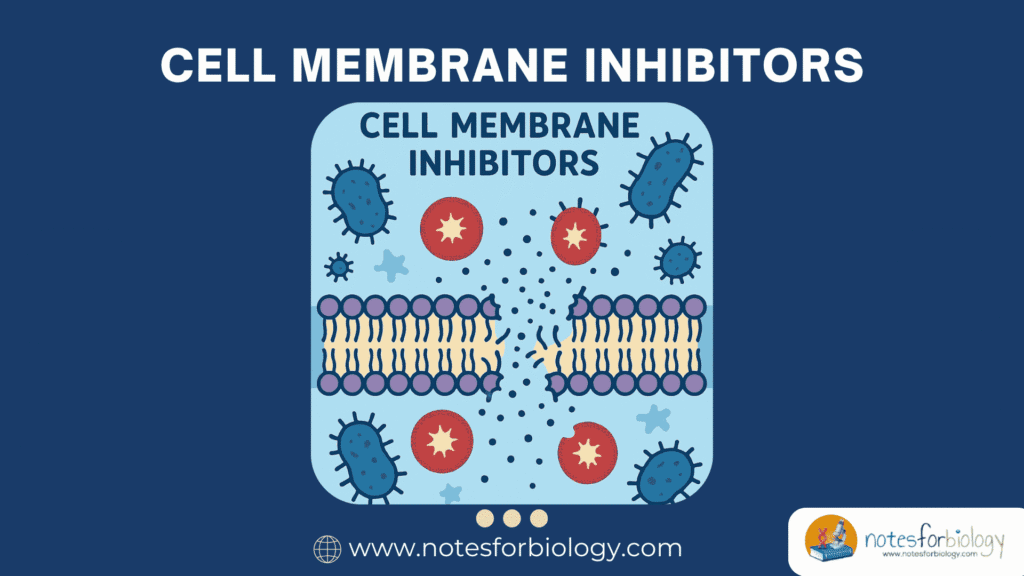
Cell Membrane Inhibitors: Examples, Inhibition, Resistance
Cell membrane inhibitors are a specialized class of antimicrobial agents that exert their action by targeting the integrity, structure, or function of microbial cell membranes. These inhibitors cause disruption of membrane permeability, leakage of intracellular contents, and eventual cell death. This mechanism is particularly valuable because the cell membrane is essential for maintaining the ionic […]
Cell Membrane Inhibitors: Examples, Inhibition, Resistance Read More »