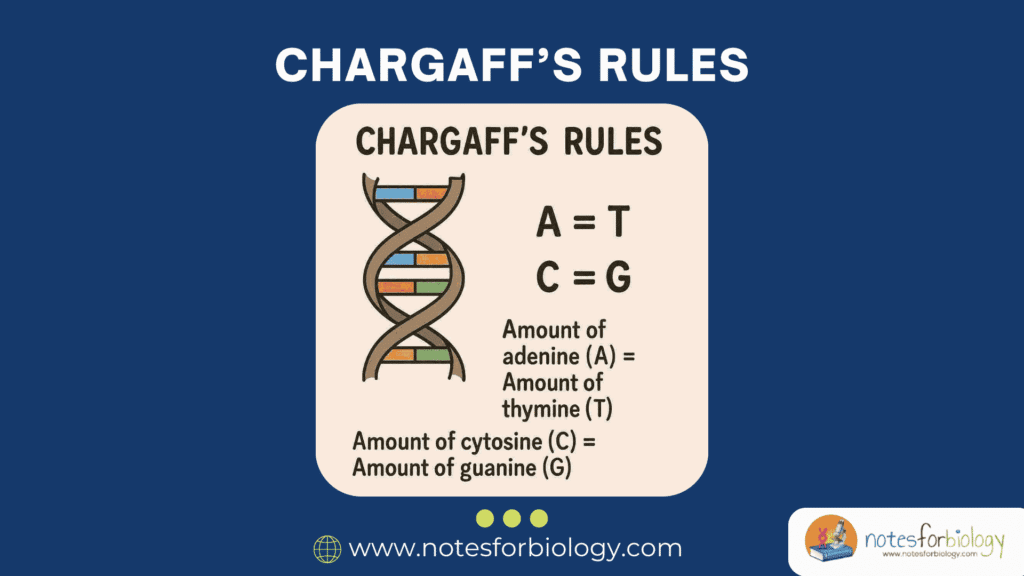
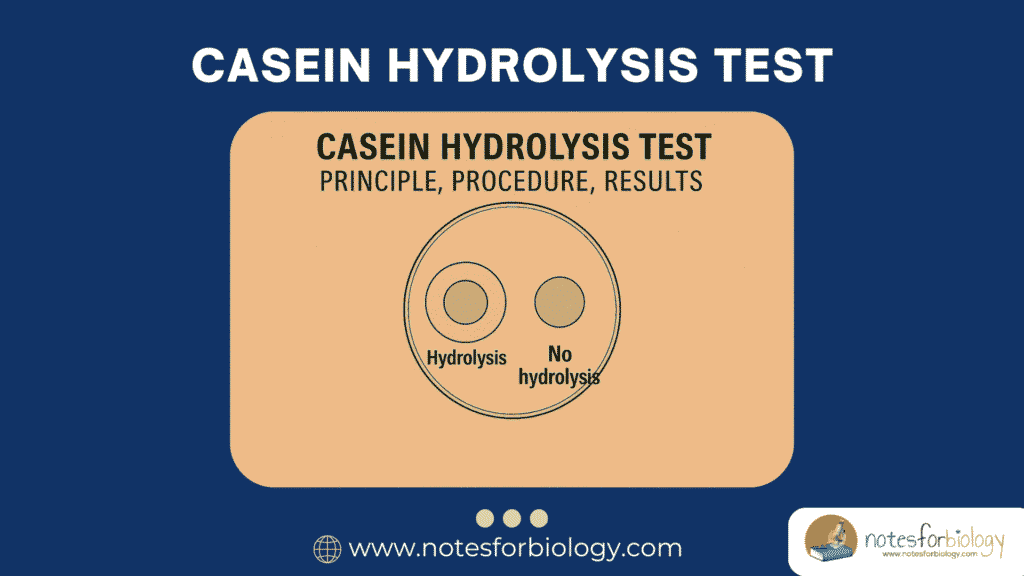
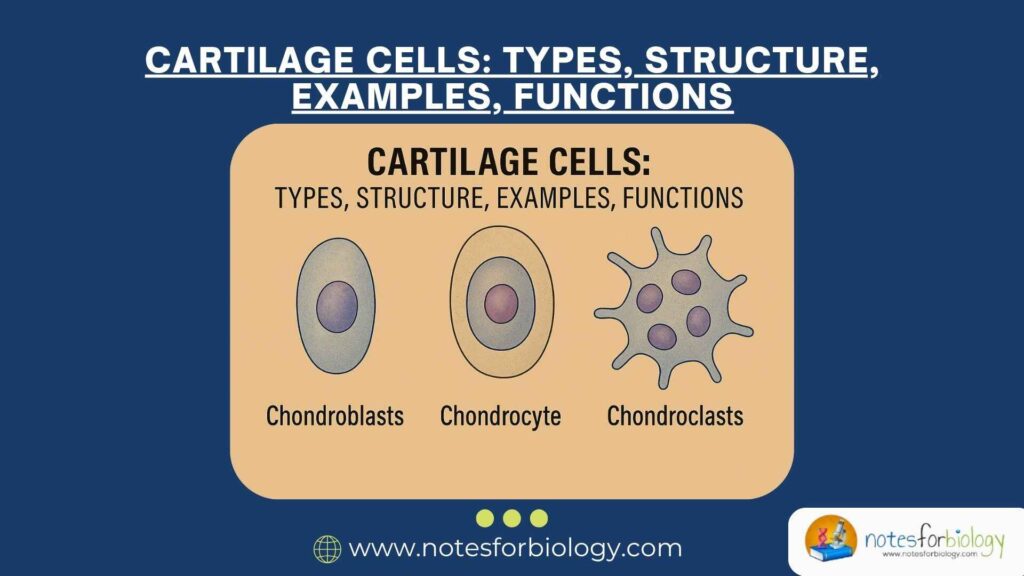
Chargaff’s Rules: First and Second Rules, Applications
The structure and composition of DNA have long fascinated scientists, especially since it is the molecule responsible for carrying genetic information in all living organisms. Understanding the chemical nature and arrangement of DNA was crucial in laying the groundwork for molecular biology and genetics as scientific disciplines. A key breakthrough in this area came with […]
Chargaff’s Rules: First and Second Rules, Applications Read More »